Dissection of the genetics of Parkinson's disease identifies an additional association 5' of SNCA and multiple associated haplotypes at 17q21
- PMID: 21044948
- PMCID: PMC3005904
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq469
Dissection of the genetics of Parkinson's disease identifies an additional association 5' of SNCA and multiple associated haplotypes at 17q21
Abstract
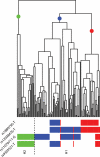
We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in 1705 Parkinson's disease (PD) UK patients and 5175 UK controls, the largest sample size so far for a PD GWAS. Replication was attempted in an additional cohort of 1039 French PD cases and 1984 controls for the 27 regions showing the strongest evidence of association (P< 10(-4)). We replicated published associations in the 4q22/SNCA and 17q21/MAPT chromosome regions (P< 10(-10)) and found evidence for an additional independent association in 4q22/SNCA. A detailed analysis of the haplotype structure at 17q21 showed that there are three separate risk groups within this region. We found weak but consistent evidence of association for common variants located in three previously published associated regions (4p15/BST1, 4p16/GAK and 1q32/PARK16). We found no support for the previously reported SNP association in 12q12/LRRK2. We also found an association of the two SNPs in 4q22/SNCA with the age of onset of the disease.
Figures

References
-
- Gilks W., Abou-Sleiman P., Gandhi S., Jain S., Singleton A., Lees A., Shaw K., Bhatia K., Bonifati V., Quinn N, et al. A common LRRK2 mutation in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2005;365:415–416. - PubMed
-
- Singleton A.B., Farrer M., Johnson J., Singleton A., Hague S., Kachergus J., Hulihan M., Peuralinna T., Dutra A., Nussbaum R., et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003;302:415–416. - PubMed
-
- Satake W., Nakabayashi Y., Mizuta I., Hirota Y., Ito C., Kubo M., Kawaguchi T., Tsunoda T., Watanabe M., Takeda A., et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1303–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- J-0804/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MC_G0901330/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000735/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 089698/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G19/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901310/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PDA/02/06/016/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- K-0905/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0800784/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 084747/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_09003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

