Activated protein C N-linked glycans modulate cytoprotective signaling function on endothelial cells
- PMID: 21044954
- PMCID: PMC3020740
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.159475
Activated protein C N-linked glycans modulate cytoprotective signaling function on endothelial cells
Abstract
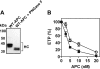
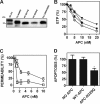
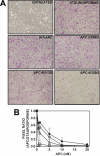
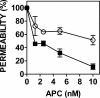
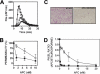
Activated protein C (APC) has potent anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties that limit clot formation, inhibit apoptosis, and protect vascular endothelial cell barrier integrity. In this study, the role of N-linked glycans in modulating APC endothelial cytoprotective signaling via endothelial cell protein C receptor/protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) was investigated. Enzymatic digestion of APC N-linked glycans (PNG-APC) decreased the APC concentration required to achieve half-maximal inhibition of thrombin-induced endothelial cell barrier permeability by 6-fold. Furthermore, PNG-APC exhibited increased protection against staurosporine-induced endothelial cell apoptosis when compared with untreated APC. To investigate the specific N-linked glycans responsible, recombinant APC variants were generated in which each N-linked glycan attachment site was eliminated. Of these, APC-N329Q was up to 5-fold more efficient in protecting endothelial barrier function when compared with wild type APC. Based on these findings, an APC variant (APC-L38D/N329Q) was generated with minimal anticoagulant activity, but 5-fold enhanced endothelial barrier protective function and 30-fold improved anti-apoptotic function when compared with wild type APC. These data highlight the previously unidentified role of APC N-linked glycosylation in modulating endothelial cell protein C receptor-dependent cytoprotective signaling via PAR1. Furthermore, our data suggest that plasma β-protein C, characterized by aberrant N-linked glycosylation at Asn-329, may be particularly important for maintenance of APC cytoprotective functions in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 5532–5535 - PubMed
-
- Fay P. J., Smudzin T. M., Walker F. J. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 20139–20145 - PubMed
-
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. (1979) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 571, 333–342 - PubMed
-
- Riewald M., Petrovan R. J., Donner A., Mueller B. M., Ruf W. (2002) Science 296, 1880–1882 - PubMed
-
- White B., Schmidt M., Murphy C., Livingstone W., O'Toole D., Lawler M., O'Neill L., Kelleher D., Schwarz H. P., Smith O. P. (2000) Br. J. Haematol. 110, 130–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

