SLUG-induced elevation of D1 cyclin in breast cancer cells through the inhibition of its ubiquitination
- PMID: 21044962
- PMCID: PMC3013006
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164384
SLUG-induced elevation of D1 cyclin in breast cancer cells through the inhibition of its ubiquitination
Abstract
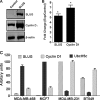
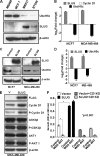
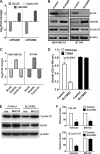
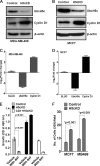
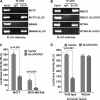
UbcH5c, a member of the UbcH5 family of protein ubiquitin conjugase E2 enzymes, is a critical component of biological processes in human cells, being the initial ubiquitinating enzyme of substrates like IκB, TP53, and cyclin D1. We report here that the metastasis regulator protein SLUG inhibits the expression of UbcH5c directly through chromatin remodeling and thus, among other downstream effects, elevates the level of cyclin D1, thus enhancing the growth rates of breast cancer cells. Overexpression of SLUG in the SLUG-deficient breast cancer cells significantly decreased the levels of mRNA and protein of UbcH5c but only elevated the protein levels of cyclin D1. On the contrary, knockdown of SLUG in SLUG-high breast cancer cells elevated the levels of UbcH5c while decreasing the level of cyclin D1 protein. SLUG is recruited at the E2-box sequence at the UbcH5c gene promoter along with the corepressor CtBP1 and the effector HDAC1 to silence the expression of this gene. Knockdown of UbcH5c in the SLUG-deficient human breast cells elevated the level of cyclin D1 as well as the rates of proliferation and invasiveness of these cells. Whereas the growth rates of the cells are enhanced due to overexpression of SLUG or knockdown of UbcH5c in the breast cancer cells tested, ER(+) cells also acquire resistance to the anti-estrogen 4-hydroxytamoxifen due to the rise of cyclin D1 levels in these cells. This study thus implicates high levels of SLUG and low levels of UbcH5c as a determinant in the progression of metastatic breast cancer.
Figures


References
-
- López-Otín C., Hunter T. (2010) Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 278–292 - PubMed
-
- Gallastegui N., Groll M. (2010) Trends Biochem. Sci. 35, 634–642 - PubMed
-
- Fang Y., Fu D., Shen X. Z. (2010) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1806, 1–6 - PubMed
-
- Pickart C. M. (2001) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 503–533 - PubMed
-
- Baek K. H. (2006) Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 7, 171–177 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

