Antibodies mediate intracellular immunity through tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21)
- PMID: 21045130
- PMCID: PMC2993423
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014074107
Antibodies mediate intracellular immunity through tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21)
Abstract
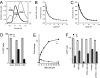
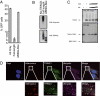
Antibodies provide effective antiviral immunity despite the fact that viruses escape into cells when they infect. Here we show that antibodies remain attached to viruses after cell infection and mediate an intracellular immune response that disables virions in the cytosol. We have discovered that cells possess a cytosolic IgG receptor, tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21), which binds to antibodies with a higher affinity than any other IgG receptor in the human body. TRIM21 rapidly recruits to incoming antibody-bound virus and targets it to the proteasome via its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Proteasomal targeting leads to rapid degradation of virions in the cytosol before translation of virally encoded genes. Infection experiments demonstrate that at physiological antibody concentrations TRIM21 neutralizes viral infection. These results reveal an intracellular arm of adaptive immunity in which the protection mediated by antibodies does not end at the cell membrane but continues inside the cell to provide a last line of defense against infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

