TRPM7 is essential for Mg(2+) homeostasis in mammals
- PMID: 21045827
- PMCID: PMC3060619
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1108
TRPM7 is essential for Mg(2+) homeostasis in mammals
Abstract
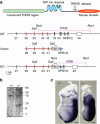
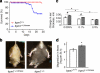
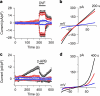
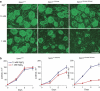
Mg(2+) is the second-most abundant cation in animal cells and is an essential cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions. The molecular mechanisms controlling Mg(2+) balance in the organism are not well understood. In this study, we report identification of TRPM7, a bifunctional protein containing a protein kinase fused to an ion channel, as a key regulator of whole body Mg(2+) homeostasis in mammals. We generated TRPM7-deficient mice with the deletion of the kinase domain. Homozygous TRPM7(Δkinase) mice demonstrated early embryonic lethality, whereas heterozygous mice were viable, but developed signs of hypomagnesaemia and revealed a defect in intestinal Mg(2+) absorption. Cells derived from heterozygous TRPM7(Δkinase) mice demonstrated reduced TRPM7 currents that had increased sensitivity to the inhibition by Mg(2+). Embryonic stem cells lacking TRPM7 kinase domain displayed a proliferation arrest phenotype that can be rescued by Mg(2+) supplementation. Our results demonstrate that TRPM7 is essential for the control of cellular and whole body Mg(2+) homeostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Schmitz C. et al.. Regulation of vertebrate cellular Mg2+ homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell 114, 191–200 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Runnels L. W., Yue L. & Clapham D. E. TRP-PLIK, a bifunctional protein with kinase and ion channel activities. Science 291, 1043–1047 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Nadler M. J. et al.. LTRPC7 is a Mg.ATP-regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature 411, 590–595 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Schlingmann K. P. et al.. Hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia is caused by mutations in TRPM6, a new member of the TRPM gene family. Nat. Genet. 31, 166–170 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Walder R. Y. et al.. Mutation of TRPM6 causes familial hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia. Nat. Genet. 31, 171–174 (2002). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

