The impact of an aromatase inhibitor on body composition and gonadal hormone levels in women with breast cancer
- PMID: 21046232
- PMCID: PMC3103776
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-010-1223-2
The impact of an aromatase inhibitor on body composition and gonadal hormone levels in women with breast cancer
Abstract
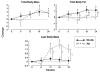
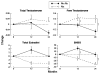
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) have become the standard adjuvant therapy of postmenopausal breast cancer survivors. AIs induce a reduction of bioavailable estrogens by inhibiting aromatase, which would be expected to induce alterations in body composition, more extensive than induced by menopause. The objectives are to examine the impact of AIs on (1) DXA-scan derived body composition and (2) gonadal hormone levels. This is a sub-analysis of a 2-year double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of 82 women with nonmetastatic breast cancer, newly menopausal following chemotherapy, who were randomized to risedronate (35 mg once weekly) versus placebo, and stratified for their usage of AI versus no AI. Outcomes included DXA-scan derived body composition and gonadal hormone levels. As a group, total body mass increased in women over 24 months. Women on AIs gained a significant amount of lean body mass compared to baseline as well as to no-AI users (P < 0.05). Women not on an AI gained total body fat compared to baseline and AI users (P < 0.05). Free testosterone significantly increased and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) significantly decreased in women on AIs compared to no AIs at 24 months (P < 0.01) while total estradiol and testosterone levels remained stable. Independent of AI usage, chemotherapy-induced postmenopausal breast cancer patients demonstrated an increase of total body mass. AI users demonstrated maintenance of total body fat, an increase in lean body mass and free testosterone levels, and a decrease in SHBG levels compared to no-AI users. The mechanisms and implications of these changes need to be studied further.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Smith IE, Dowsett M. Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(24):2431–2442. - PubMed
-
- Dowsett M, Cuzick J, Ingle J, Coates A, Forbes J, Bliss J, Buyse M, Baum M, Buzdar A, Colleoni M, et al. Meta-analysis of breast cancer outcomes in adjuvant trials of aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(3):509–518. - PubMed
-
- Carr MC. The emergence of the metabolic syndrome with menopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(6):2404–2411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

