Man's best friend becomes biology's best in show: genome analyses in the domestic dog
- PMID: 21047261
- PMCID: PMC3322674
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102808-115200
Man's best friend becomes biology's best in show: genome analyses in the domestic dog
Abstract
In the last five years, canine genetics has gone from map construction to complex disease deconstruction. The availability of a draft canine genome sequence, dense marker chips, and an understanding of the genome architecture has changed the types of studies canine geneticists can undertake. There is now a clear recognition that the dog system offers the opportunity to understand the genetics of both simple and complex traits, including those associated with morphology, disease susceptibility, and behavior. In this review, we summarize recent findings regarding canine domestication and review new information on the organization of the canine genome. We discuss studies aimed at finding genes controlling morphological phenotypes and provide examples of the way such paradigms may be applied to studies of behavior. We also discuss the many ways in which the dog has illuminated our understanding of human disease and conclude with a discussion on where the field is likely headed in the next five years.
Figures
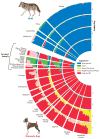

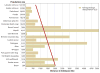
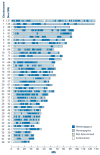


References
-
- Agnarsson I, Kuntner M, May-Collado LJ. Dogs, cats, and kin: a molecular species-level phylogeny of Carnivora. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2009;54:726–45. - PubMed
-
- American Kennel Club. Breed Registry Data Base. New York: AKC; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

