The RecQ DNA helicases in DNA repair
- PMID: 21047263
- PMCID: PMC4038414
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163602
The RecQ DNA helicases in DNA repair
Abstract
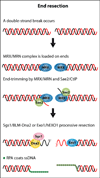
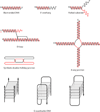
The RecQ helicases are conserved from bacteria to humans and play a critical role in genome stability. In humans, loss of RecQ gene function is associated with cancer predisposition and/or premature aging. Recent experiments have shown that the RecQ helicases function during distinct steps during DNA repair; DNA end resection, displacement-loop (D-loop) processing, branch migration, and resolution of double Holliday junctions (dHJs). RecQ function in these different processing steps has important implications for its role in repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) that occur during DNA replication and meiosis, as well as at specific genomic loci such as telomeres.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad F, Stewart E. The N-terminal region of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe RecQ helicase, Rqh1p, physically interacts with Topoisomerase III and is required for Rqh1p function. Mol. Genet. Genomics. 2005;273:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Bae SH, Bae KH, Kim JA, Seo YS. RPA governs endonuclease switching during processing of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes. Nature. 2001;412:456–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

