Pseudogenes as an alternative source of natural antisense transcripts
- PMID: 21047404
- PMCID: PMC2984423
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-338
Pseudogenes as an alternative source of natural antisense transcripts
Abstract
Background: Naturally occurring antisense transcripts (NATs) are non-coding RNAs that may regulate the activity of sense transcripts to which they bind because of complementarity. NATs that are not located in the gene they regulate (trans-NATs) have better chances to evolve than cis-NATs, which is evident when the sense strand of the cis-NAT is part of a protein coding gene. However, the generation of a trans-NAT requires the formation of a relatively large region of complementarity to the gene it regulates.
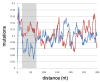
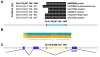
Results: Pseudogene formation may be one evolutionary mechanism that generates trans-NATs to the parental gene. For example, this could occur if the parental gene is regulated by a cis-NAT that is copied as a trans-NAT in the pseudogene. To support this we identified human pseudogenes with a trans-NAT to the parental gene in their antisense strand by analysis of the database of expressed sequence tags (ESTs). We found that the mutations that appeared in these trans-NATs after the pseudogene formation do not show the flat distribution that would be expected in a non functional transcript. Instead, we found higher similarity to the parental gene in a region nearby the 3' end of the trans-NATs.
Conclusions: Our results do not imply a functional relation of the trans-NAT arising from pseudogenes over their respective parental genes but add evidence for it and stress the importance of duplication mechanisms of genetic material in the generation of non-coding RNAs. We also provide a plausible explanation for the large transcripts that can be found in the antisense strand of some pseudogenes.
Figures

References
-
- Xie Z, Qi X. Diverse small RNA-directed silencing pathways in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779(11):720–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

