Application of smart phone in "Better Border Healthcare Program": a module for mother and child care
- PMID: 21047412
- PMCID: PMC2989931
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-69
Application of smart phone in "Better Border Healthcare Program": a module for mother and child care
Abstract
Background: To assess the application of cell phone integrating into the healthcare system to improve antenatal care (ANC) and expanded programme on immunization (EPI) services for the under-served population in border area.
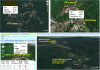
Methods: A module combining web-based and mobile technology was developed to generate ANC/EPI visit schedule dates in which the healthcare personnel can cross-check, identify and update the mother's ANC and child's EPI status at the healthcare facility or at the household location when performing home visit; with additional feature of sending appointment reminder directly to the scheduled mother in the community.
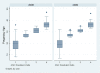
Results: The module improved ANC/EPI coverage in the study area along the country border including for both Thai and non-Thai mothers and children who were either permanent resident or migrants; numbers of ANC and EPI visit on-time as per schedule significantly increased; there was less delay of antenatal visits and immunizations.
Conclusions: The module integrated and functioned successfully as part of the healthcare system; it is proved for its feasibility and the extent to which community healthcare personnel in the low resource setting could efficiently utilize it to perform their duties.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations. The Millennium Development Goals Report. 2009. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/mdg/Resources/Static/Products/Progress2009/MD...
-
- Say L, Newby H. Millennium Development Goals Indicators: Goal 5. Improve maternal health. 2010. http://unstats.un.org
-
- USAID. Focused Antenatal Care: Providing integrated, individualized care during pregnancy. 2010. http://maternalhealthtaskforce.org/library/doc_details/582-focused-anten...
-
- Sawasleemongkol S, (Editor) "Antenatal Care" In Obstetrics (Thai) Bangkok. 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical