Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by related allografts in hematologic malignancies: long-term outcomes most successful in indolent and aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- PMID: 21047561
- PMCID: PMC4082980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.10.030
Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by related allografts in hematologic malignancies: long-term outcomes most successful in indolent and aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Abstract
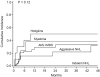
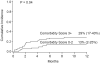
Reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) extends the curative potential of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) to patients with hematologic malignancies unable to withstand myeloablative conditioning. We prospectively analyzed the outcomes of 123 patients (median age, 57 years; range, 23-70 years) with hematologic malignancies treated with a uniform RIC regimen of cyclophosphamide, fludarabine, and total-body irradiation (200 cGy) with or without antithymocyte globulin followed by related donor allogeneic HCT at the University of Minnesota between 2002 and 2008. The cohort included 45 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), 27 with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), 8 with indolent NHL, 10 with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), 10 with myeloma, and 23 with acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, other leukemias, or myeloproliferative disorders. The probability of 4-year overall survival was 73% for patients with indolent NHL, 58% for those with aggressive NHL, 67% for those with HL, 30% for those with AML/MDS, and only 10% for those with myeloma. Corresponding outcomes for relapse in these patients were 0%, 32%, 50%, 33%, and 38%, and those for progression-free survival were 73%, 45%, 27%, 27%, and 10%. The incidence of treatment-related mortality was 14% at day +100 and 22% at 1 year. The incidence of grade II-IV acute graft-versus-host disease was 38% at day +100, and that of chronic graft-versus-host disease was 50% at 2 years. Multivariate analysis revealed superior overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with both indolent and aggressive NHL compared with those with AML/MDS, HL, or myeloma. Worse 1-year treatment-related mortality was observed in patients with a Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index score ≥ 3 and in cytomegalovirus-seropositive recipients. These results suggest that (1) RIC conditioning was well tolerated by an older, heavily pretreated population; (2) patients with indolent and aggressive NHL respond well to RIC conditioning, highlighting the importance of the graft-versus-lymphoma effect; and (3) additional peri-transplantation manipulations are needed to improve outcomes for patients with AML/MDS or myeloma receiving RIC conditioning before HCT.
2011 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, et al. Retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2006;108:836–846. - PubMed
-
- Martino R, Valcarcel D, Brunet S, Sureda A, Sierra J. Comparable non-relapse mortality and survival after HLA-identical sibling blood stem cell transplantation with reduced or conventional-intensity preparative regimens for high-risk myelodysplasia or acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;41:33–38. - PubMed
-
- Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Yerushalmi R, Nagler A. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in AML and MDS using myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning: long-term follow-up. Leukemia. 2010;24:1050–1052. - PubMed
-
- Alyea EP, Kim HT, Ho V, et al. Impact of conditioning regimen intensity on outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for advanced acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Biol.Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12:1047–1055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous