Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and recombination between HBV genotypes D and E in asymptomatic blood donors from Khartoum, Sudan
- PMID: 21048009
- PMCID: PMC3020474
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00867-10
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and recombination between HBV genotypes D and E in asymptomatic blood donors from Khartoum, Sudan
Abstract
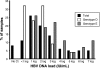
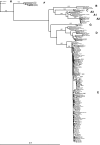
Sudan is a highly endemic area for hepatitis B virus (HBV), and >5% of blood donors are chronically infected. To examine potential strategies to improve HBV blood safety, 404 replacement donor samples previously screened for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) were tested for antibody to HBV core (anti-HBc), anti-surface antigen (anti-HBs), and HBV DNA. Of 145 anti-HBc-containing samples (36%) identified, 16 retested were HBsAg positive (11%). Anti-HBs was detected in 43/77 (56%) anti-HBc-reactive samples. Six samples were HBsAg(-)/anti-HBc(+)/anti-HBs(+) and contained HBV DNA, meeting the definition of occult HBV infection (OBI). OBIs had low HBV DNA loads (<10 IU/ml) and were genotype B (n = 1) or genotype D (n = 5). Pre-S/S and/or whole genome sequences were obtained from 47 randomly selected HBsAg-positive donors added to the previous 16. Genotype E was identified in 27 strains (57.5%), genotype D in 19 strains (40.5%), and genotype A2 in 1 strain (2%). Two outlier strains within genotype D ultimately were identified as recombinants of genotypes D and E with identical recombination points, suggesting circulating, infectious, recombinant strains. Anti-HBc screening does not appear to be a sustainable blood safety strategy because of the cost and the negative impact on the Sudanese blood supply, even when reduced by anti-HBs testing. Being at the junction between two main African HBV genotypes, genetic recombination occurred and became part of the molecular epidemiology of HBV in Sudan.
Figures


References
-
- Allain, J.-P. 2004. Occult hepatitis B virus infection: implications in transfusion. Vox Sang. 86:83-91. - PubMed
-
- Allain, J.-P., D. Belkhiri, M. Vermeulen, R. Crookes, R. Cable, A. Amiri, R. Reddy, A. Bird, and D. Candotti. 2009. Characterization of occult hepatitis B virus strains in South African blood donors. Hepatology 49:1868-1876. - PubMed
-
- Allain, J.-P., D. Candotti, K. Soldan, F. Sarkodie, B. Phelps, C. Giachetti, V. Shyamala, F. Yeboah, M. Anokwa, S. Owusu-Ofori, and O. Opare-Sem. 2003. The risk of hepatitis B virus infection by transfusion in Kumasi, Ghana. Blood 101:2419-2425. - PubMed
-
- Behzad-Behbahani, A., A. Mafi-Nejad, S. Z. Tabei, K. B. Lankarani, A. Torab, and A. Moaddeb. 2006. Anti-HBc & HBV DNA detection in blood donors negative for hepatitis B virus surface antigen in reducing risk of transfusion associated HBV infection. Indian J. Med. Res. 123:37-42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

