LysGH15, a novel bacteriophage lysin, protects a murine bacteremia model efficiently against lethal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection
- PMID: 21048011
- PMCID: PMC3020447
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01144-10
LysGH15, a novel bacteriophage lysin, protects a murine bacteremia model efficiently against lethal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection
Abstract
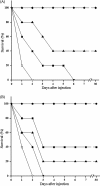
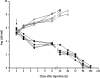
Phage-coded lysin is an enzyme that destroys the cell walls of bacteria. Phage lysin could be an alternative to conventional antibiotic therapy against pathogens that are resistant to multiple antibiotics. In this study, a novel staphylococcal phage, GH15, was isolated, and the endogenous lytic enzyme (LysGH15) was expressed and purified. The lysin LysGH15 displayed a broad lytic spectrum; in vitro treatment killed a number of Staphylococcus aureus strains rapidly and completely, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). In animal experiments, a single intraperitoneal injection of LysGH15 (50 μg) administered 1 h after MRSA injections at double the minimum lethal dose was sufficient to protect mice (P < 0.01). Bacteremia in unprotected mice reached colony counts of about 10(7) CFU/ml within 3.5 h after challenge, whereas the mean colony count in lysin-protected mice was less than 10(4) CFU/ml (and ultimately became undetectable). These results indicate that LysGH15 can kill S. aureus in vitro and can protect mice efficiently from bacteremia in vivo. The phage lysin LysGH15 might be an alternative treatment strategy for infections caused by MRSA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Effects of Phage Lysin LysGH15 on Planktonic Cells and Biofilms of Diverse Staphylococci.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;84(15):e00886-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00886-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29776929 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy of LysGH15 and Apigenin as a New Strategy for Treating Pneumonia Caused by Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Oct 16;82(1):87-94. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02581-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26475103 Free PMC article.
-
LysGH15 kills Staphylococcus aureus without being affected by the humoral immune response or inducing inflammation.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 7;6:29344. doi: 10.1038/srep29344. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27385518 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update on New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;34(4):849-861. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33011050 Review.
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016 Jun;30(2):491-507. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.02.009. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27208769 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of the virion-associated peptidoglycan hydrolase HydH5 and its derivative fusion proteins in milk biopreservation.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054828. Epub 2013 Jan 24. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23359813 Free PMC article.
-
Nonconventional Therapeutics against Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Nov;6(6):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0047-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0047-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30547858 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic and genomic characterization of a novel virulent Aeromonas hydrophila phage phiA051, with high homology to prophages.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 18;11:1415685. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1415685. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39091387 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and Genetic Characterization of Eggerthella lenta Bacteriophage PMBT5.Viruses. 2022 Jul 22;14(8):1598. doi: 10.3390/v14081598. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35893664 Free PMC article.
-
An Enzybiotic Regimen for the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Orthopaedic Device-Related Infection.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;10(10):1186. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10101186. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borysowski, J., B. Weber-Dabrowska, and A. Gorski. 2006. Bacteriophage endolysins as a novel class of antibacterial agents. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 231:366-377. - PubMed
-
- Brumfitt, W., and J. Hamilton-Miller. 1989. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N. Engl. J. Med. 320:1188-1196. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, Q., and V. A. Fischetti. 2007. Mutagenesis of a bacteriophage lytic enzyme PlyGBS significantly increases its antibacterial activity against group B streptococci. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74:1284-1291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

