The European LeukemiaNet: achievements and perspectives
- PMID: 21048032
- PMCID: PMC3012780
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.032979
The European LeukemiaNet: achievements and perspectives
Abstract
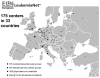
The only way to cure leukemia is by cooperative research. To optimize research, the European LeukemiaNet integrates 105 national leukemia trial groups and networks, 105 interdisciplinary partner groups and about 1,000 leukemia specialists from 175 institutions. They care for tens of thousands of leukemia patients in 33 countries across Europe. Their ultimate goal is to cure leukemia. Since its inception in 2002, the European LeukemiaNet has steadily expanded and has unified leukemia research across Europe. The European LeukemiaNet grew from two major roots: 1) the German Competence Network on Acute and Chronic Leukemias; and 2) the collaboration of European Investigators on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. The European LeukemiaNet has improved leukemia research and management across Europe. Its concept has led to funding by the European Commission as a network of excellence. Other sources (European Science Foundation; European LeukemiaNet-Foundation) will take over when the support of the European Commission ends.
Figures

References
-
- Hehlmann R, Berger U, Aul C, Büchner T, Döhner H, Ehninger G, et al. The German competence network ‘Acute and chronic leukemias’. Leukemia. 2004;18(4):665–9. - PubMed
-
- Baccarani M, Saglio G, Goldman J, Hochhaus A, Simonsson B, Appelbaum F, et al. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia. Recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2006;108(6):1809–20. - PubMed
-
- Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A, Baccarani M. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2007;370:342–50. - PubMed
-
- Müller MC, Cross NC, Erben P, Schenk T, Hanfstein B, Ernst T, et al. Harmonization of molecular monitoring of CML therapy in Europe. Leukemia. 2009;23(11):1957–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

