Chronic spontaneous activity generated in the somata of primary nociceptors is associated with pain-related behavior after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 21048146
- PMCID: PMC3073589
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2428-10.2010
Chronic spontaneous activity generated in the somata of primary nociceptors is associated with pain-related behavior after spinal cord injury
Abstract
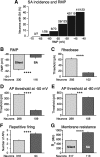
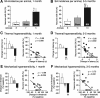
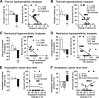
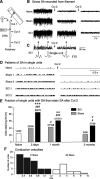
Mechanisms underlying chronic pain that develops after spinal cord injury (SCI) are incompletely understood. Most research on SCI pain mechanisms has focused on neuronal alterations within pain pathways at spinal and supraspinal levels associated with inflammation and glial activation. These events might also impact central processes of primary sensory neurons, triggering in nociceptors a hyperexcitable state and spontaneous activity (SA) that drive behavioral hypersensitivity and pain. SCI can sensitize peripheral fibers of nociceptors and promote peripheral SA, but whether these effects are driven by extrinsic alterations in surrounding tissue or are intrinsic to the nociceptor, and whether similar SA occurs in nociceptors in vivo are unknown. We show that small DRG neurons from rats (Rattus norvegicus) receiving thoracic spinal injury 3 d to 8 months earlier and recorded 1 d after dissociation exhibit an elevated incidence of SA coupled with soma hyperexcitability compared with untreated and sham-treated groups. SA incidence was greatest in lumbar DRG neurons (57%) and least in cervical neurons (28%), and failed to decline over 8 months. Many sampled SA neurons were capsaicin sensitive and/or bound the nociceptive marker, isolectin B4. This intrinsic SA state was correlated with increased behavioral responsiveness to mechanical and thermal stimulation of sites below and above the injury level. Recordings from C- and Aδ-fibers revealed SCI-induced SA generated in or near the somata of the neurons in vivo. SCI promotes the entry of primary nociceptors into a chronic hyperexcitable-SA state that may provide a useful therapeutic target in some forms of persistent pain.
Figures


References
-
- Abram SE, Yi J, Fuchs A, Hogan QH. Permeability of injured and intact peripheral nerves and dorsal root ganglia. Anesthesiology. 2006;105:146–153. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Ringkamp M, Hartke TV, Chien HF, Flavahan NA, Campbell JN, Meyer RA. Uninjured C-fiber nociceptors develop spontaneous activity and alpha-adrenergic sensitivity following L6 spinal nerve ligation in monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:455–466. - PubMed
-
- Amir R, Devor M. Ongoing activity in neuroma afferents bearing retrograde sprouts. Brain Res. 1993;630:283–288. - PubMed
-
- Andersen OK, Finnerup NB, Spaich EG, Jensen TS, Arendt-Nielsen L. Expansion of nociceptive withdrawal reflex receptive fields in spinal cord injured humans. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115:2798–2810. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
