Flagellin as an adjuvant: cellular mechanisms and potential
- PMID: 21048152
- PMCID: PMC3756556
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002156
Flagellin as an adjuvant: cellular mechanisms and potential
Abstract
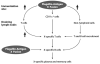
Flagellin is a potent activator of a broad range of cell types involved in innate and adaptive immunity. An increasing number of studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of flagellin as an adjuvant, as well as its ability to promote cytokine production by a range of innate cell types, trigger a generalized recruitment of T and B lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid sites, and activate TLR5(+)CD11c(+) cells and T lymphocytes in a manner that is distinct from cognate Ag recognition. The plasticity of flagellin has allowed for the generation of a range of flagellin-Ag fusion proteins that have proven to be effective vaccines in animal models. This review summarizes the state of our current understanding of the adjuvant effect of flagellin and addresses important areas of current and future research interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Flagellin as an adjuvant: cellular mechanisms and potential".J Immunol. 2011 Feb 1;186(3):1299; author reply 1299. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1090134. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21248266 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 2001;410:1099–1103. - PubMed
-
- Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL. Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J. Immunol. 2001;167:1882–1885. - PubMed
-
- Mizel SB, Snipes JA. Gram-negative flagellin-induced self-tolerance is associated with a block in interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase release from toll-like receptor 5. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:22414–22420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

