Integration of image exposure time into a modified laser speckle imaging method
- PMID: 21048287
- PMCID: PMC3311822
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/22/016
Integration of image exposure time into a modified laser speckle imaging method
Abstract
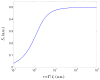
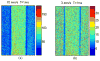
Speckle-based methods have been developed to characterize tissue blood flow and perfusion. One such method, called modified laser speckle imaging (mLSI), enables computation of blood flow maps with relatively high spatial resolution. Although it is known that the sensitivity and noise in LSI measurements depend on image exposure time, a fundamental disadvantage of mLSI is that it does not take into account this parameter. In this work, we integrate the exposure time into the mLSI method and provide experimental support of our approach with measurements from an in vitro flow phantom.
Figures
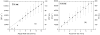
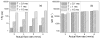
References
-
- Ayata C, Dunn AK, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Huang Z, Boas DA, Moskowitz MA. Laser speckle flowmetry for the study of cerebrovascular physiology in normal and ischemic mouse cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay R, Gittings AS, Suh SS, Dixon PK, Durian DJ. Speckle-visibility spectroscopy: a tool to study time-varying dynamics. Rev Sci Instrum. 2005;76:093110.
-
- Bolay H, Reuter U, Dunn AK, Huang ZH, Boas DA, Moskowitz MA. Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat Med. 2002;8:136–42. - PubMed
-
- Briers JD, Richards G, He XW. Capillary blood flow monitoring using laser speckle contrast analysis (LASCA) J Biomed Opt. 1999;4:164–75. - PubMed
