Epigenetic regulation of immune cell functions during post-septic immunosuppression
- PMID: 21048427
- PMCID: PMC3092675
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.6.3.14017
Epigenetic regulation of immune cell functions during post-septic immunosuppression
Abstract
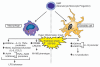
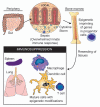
Studies in humans and animal models indicate that profound immunosuppression is one of the chronic consequences of severe sepsis. This immune dysfunction encompasses deficiencies in activation of cells in both the myeloid and lymphoid cell lineages. As a result, survivors of severe sepsis are at risk of succumbing to infections perpetrated by opportunistic pathogens that are normally controlled by a fully functioning immune system. Recent studies have indicated that epigenetic mechanisms may be one driving force behind this immunosuppression, through suppression of proinflammatory gene production and subsequent immune cell activation, proliferation and effector function. A better understanding of epigenetics and post-septic immunosuppression can improve our diagnostic tools and may be an important potential source of novel molecular targets for new therapies. This review will discuss important pathways of immune cell activation affected by severe sepsis, and highlight pathways of epigenetic regulation that may be involved in post-septic immunosuppression.
Figures

References
-
- Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, Gerlach H, Calandra T, Cohen J, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:858–873. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1368–1377. - PubMed
-
- Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: A trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1244–1250. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
