The roles of dopamine and related compounds in reward-seeking behavior across animal phyla
- PMID: 21048897
- PMCID: PMC2967375
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2010.00163
The roles of dopamine and related compounds in reward-seeking behavior across animal phyla
Abstract
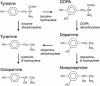
Motile animals actively seek out and gather resources they find rewarding, and this is an extremely powerful organizer and motivator of animal behavior. Mammalian studies have revealed interconnected neurobiological systems for reward learning, reward assessment, reinforcement and reward-seeking; all involving the biogenic amine dopamine. The neurobiology of reward-seeking behavioral systems is less well understood in invertebrates, but in many diverse invertebrate groups, reward learning and responses to food rewards also involve dopamine. The obvious exceptions are the arthropods in which the chemically related biogenic amine octopamine has a greater effect on reward learning and reinforcement than dopamine. Here we review the functions of these biogenic amines in behavioral responses to rewards in different animal groups, and discuss these findings in an evolutionary context.
Keywords: biogenic amine; catecholamine; dopamine; motivation; nucleus accumbens; octopamine; reward.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cocaine affects foraging behaviour and biogenic amine modulated behavioural reflexes in honey bees.PeerJ. 2014 Nov 13;2:e662. doi: 10.7717/peerj.662. eCollection 2014. PeerJ. 2014. PMID: 25405075 Free PMC article.
-
Effort-related functions of nucleus accumbens dopamine and associated forebrain circuits.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Apr;191(3):461-82. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0668-9. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17225164 Review.
-
The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999 Dec;31(1):6-41. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00023-5. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999. PMID: 10611493 Review.
-
Compromised Dopaminergic Encoding of Reward Accompanying Suppressed Willingness to Overcome High Effort Costs Is a Prominent Prodromal Characteristic of the Q175 Mouse Model of Huntington's Disease.J Neurosci. 2016 May 4;36(18):4993-5002. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0135-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27147652 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of basal ganglia and orbitofrontal cortex in goal-directed behavior.Prog Brain Res. 2000;126:193-215. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)26015-9. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105648 Review.
Cited by
-
Noncanonical genomic imprinting in the monoamine system determines naturalistic foraging and brain-adrenal axis functions.Cell Rep. 2022 Mar 8;38(10):110500. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110500. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35263575 Free PMC article.
-
Polydopamine Doping and Pyrolysis of Cellulose Nanofiber Paper for Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Nanocarbon with Improved Yield and Capacitive Performances.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;11(12):3249. doi: 10.3390/nano11123249. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947598 Free PMC article.
-
Active Inferants: An Active Inference Framework for Ant Colony Behavior.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Jun 24;15:647732. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.647732. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34248515 Free PMC article.
-
The decision to fight or flee - insights into underlying mechanism in crickets.Front Neurosci. 2012 Aug 21;6:118. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00118. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22936896 Free PMC article.
-
Reward boosts reinforcement-based motor learning.iScience. 2021 Jul 7;24(7):102821. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102821. eCollection 2021 Jul 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34345810 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

