Muscle wasting and impaired myogenesis in tumor bearing mice are prevented by ERK inhibition
- PMID: 21048967
- PMCID: PMC2965098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013604
Muscle wasting and impaired myogenesis in tumor bearing mice are prevented by ERK inhibition
Abstract
Background: The onset of cachexia is a frequent feature in cancer patients. Prominent characteristic of this syndrome is the loss of body and muscle weight, this latter being mainly supported by increased protein breakdown rates. While the signaling pathways dependent on IGF-1 or myostatin were causally involved in muscle atrophy, the role of the Mitogen-Activated-Protein-Kinases is still largely debated. The present study investigated this point on mice bearing the C26 colon adenocarcinoma.
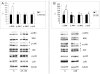
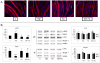
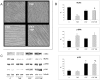
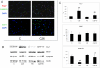
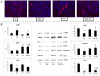
Methodology/principal findings: C26-bearing mice display a marked loss of body weight and muscle mass, this latter associated with increased phosphorylated (p)-ERK. Administration of the ERK inhibitor PD98059 to tumor bearers attenuates muscle depletion and weakness, while restoring normal atrogin-1 expression. In C26 hosts, muscle wasting is also associated with increased Pax7 expression and reduced myogenin levels. Such pattern, suggestive of impaired myogenesis, is reversed by PD98059. Increased p-ERK and reduced myosin heavy chain content can be observed in TNFα-treated C2C12 myotubes, while decreased myogenin and MyoD levels occur in differentiating myoblasts exposed to the cytokine. All these changes are prevented by PD98059.
Conclusions/significance: These results demonstrate that ERK is involved in the pathogenesis of muscle wasting in cancer cachexia and could thus be proposed as a therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Acharyya S, Guttridge DC. Cancer cachexia signaling pathways continue to emerge yet much still points to the proteasome. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1356–1361. - PubMed
-
- Hasselgren PO, Wray C, Mammen J. Molecular regulation of muscle cachexia: it may be more than the proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, Masiero E, Rudolf R, et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007;6:458–471. - PubMed
-
- Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M, Baracos V, et al. Multiple types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 2004;18:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Madrid LV, Wang CY, Baldwin AS., Jr NF-kappaB-induced loss of MyoD messenger RNA: possible role in muscle decay and cachexia. Science. 2000;289:2363–2366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

