iCLIP predicts the dual splicing effects of TIA-RNA interactions
- PMID: 21048981
- PMCID: PMC2964331
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000530
iCLIP predicts the dual splicing effects of TIA-RNA interactions
Abstract
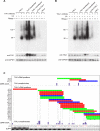
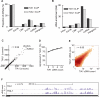
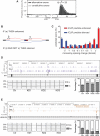
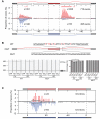
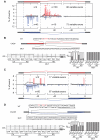
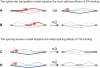
The regulation of alternative splicing involves interactions between RNA-binding proteins and pre-mRNA positions close to the splice sites. T-cell intracellular antigen 1 (TIA1) and TIA1-like 1 (TIAL1) locally enhance exon inclusion by recruiting U1 snRNP to 5' splice sites. However, effects of TIA proteins on splicing of distal exons have not yet been explored. We used UV-crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (iCLIP) to find that TIA1 and TIAL1 bind at the same positions on human RNAs. Binding downstream of 5' splice sites was used to predict the effects of TIA proteins in enhancing inclusion of proximal exons and silencing inclusion of distal exons. The predictions were validated in an unbiased manner using splice-junction microarrays, RT-PCR, and minigene constructs, which showed that TIA proteins maintain splicing fidelity and regulate alternative splicing by binding exclusively downstream of 5' splice sites. Surprisingly, TIA binding at 5' splice sites silenced distal cassette and variable-length exons without binding in proximity to the regulated alternative 3' splice sites. Using transcriptome-wide high-resolution mapping of TIA-RNA interactions we evaluated the distal splicing effects of TIA proteins. These data are consistent with a model where TIA proteins shorten the time available for definition of an alternative exon by enhancing recognition of the preceding 5' splice site. Thus, our findings indicate that changes in splicing kinetics could mediate the distal regulation of alternative splicing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Reed R. Mechanisms of fidelity in pre-mRNA splicing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe B. J. Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell. 2006;126:37–47. - PubMed
-
- Ule J, Stefani G, Mele A, Ruggiu M, Wang X, et al. An RNA map predicting Nova-dependent splicing regulation. Nature. 2006;444:580–586. - PubMed
-
- Tian Q, Streuli M, Saito H, Schlossman S. F, Anderson P. A polyadenylate binding protein localized to the granules of cytolytic lymphocytes induces DNA fragmentation in target cells. Cell. 1991;67:629–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

