Lack of knowledge: breast cancer and the soluble interleukin-6 receptor
- PMID: 21049067
- PMCID: PMC2931058
- DOI: 10.1159/000314248
Lack of knowledge: breast cancer and the soluble interleukin-6 receptor
Abstract
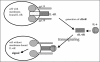
Background: Cytokines are and may be used as therapeutic targets in cancer therapy. In breast cancer, interleukin (IL)-6 is associated with different features of tumor biology like metastasis, certain stages, and decreased survival. It is now an established fact that signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) («transsignaling») is an important process in the IL-6 machinery.
Methods and results: In this mini-review, we discover that published knowledge about sIL-6R serum levels in breast cancer patients is sparse and, furthermore, most in vitro data merely show that tumor cells produce the sIL-6R endogenously.
Conclusions: Therefore, a lot of research is still necessary to analyze the significance of the sIL-6R and therefore the transsignaling process in breast tumors. More knowledge about the sIL-6R in breast cancer would give insights into its putative role as blood marker of active tumor disease. Secondly, the sIL-6R may be useful in breast cancer as a new therapeutic pathway. If, as suggested by the literature, IL-6 mediates the aggressiveness and the growth of breast tumors, elevated circulating levels of IL-6 and its receptor may identify patients for whom the IL-6 complex is a therapeutic target.
Hintergrund: In der Krebstherapie stellen Zytokine therapeutische Angriffsziele, sogenannte Targets, dar. Beim Mammakarzinom ist ein hoher Interleukin (IL)-6-Gehalt mit verschiedenen Tumorcharakteristika wie z.B. Metastasierung, bestimmten Stadien und vermindertem Überleben assoziiert. In der Zwischenzeit hat sich herausgestellt, dass die Signalweiterleitung über den löslichen IL-6-Rezeptor (sIL-6R) (“Transsignaling”) von großer Bedeutung innerhalb des IL-6-Geschehens ist.
Methoden und ergebnisse: In diesem Mini-Review stellen wir fest, dass das publizierte Wissen über den Serumgehalt an sIL-6R bei Mammakarzinompatienten lückenhaft ist. Des Weiteren zeigen publizierte In-vitro-Daten lediglich die Tatsache, dass Tumorzellen selber den sIL-6R produzieren.
Schlussfolgerungen: Aus diesem Grunde erscheint es uns notwendig herauszufinden, welche Bedeutung der sIL-6R, und damit einhergehend der Transsignaling-Prozess, beim Mammakarzinom hat. Ein breiteres Wissen über den sIL-6R beim Brustkrebs könnte seine Rolle als eventueller Marker des aktiven Tumorgeschehens beleuchten und eine neue therapeutische Möglichkeit darstellen, zumindest für diejenigen Patienten, deren Serumgehalte an IL-6 und/oder sIL-6R erhöht sind.
Keywords: Breast cancer; IL-6; Transsignaling; sIL-6R.
Figures
References
-
- Knüpfer H, Preiss R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review) Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;102:129–135. - PubMed
-
- Taga T, Kishimoto T. gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:797–819. - PubMed
-
- Hong DS, Angelo LS, Kurzrock R. Interleukin-6 and its receptor in cancer: implications for translational therapeutics. Cancer. 2007;110:1911–1928. - PubMed
-
- Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Riviere M, Houart C, Baumann M, Fey GH, Poli V, Cortese R, Islam MQ, Levan G. The interleukin-6-dependent DNA-binding protein gene (transcription factor 5: TCF5) maps to human chromosome 20 and rat chromosome 3, the IL6 receptor locus (IL6R) to human chromosome 1 and rat chromosome 2, and the rat IL6 gene to rat chromosome 4. Genomics. 1991;10:539–546. - PubMed
-
- Kluck PM, Wiegant J, Jansen RP, Bolk MW, Raap AK, Willemze R, Landegent JE. The human interleukin-6 receptor alpha chain gene is localized on chromosome 1 band q21. Hum Genet. 1993;90:542–544. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials