Desaturation - distance ratio: a new concept for a functional assessment of interstitial lung diseases
- PMID: 21049210
- PMCID: PMC2954734
- DOI: 10.1590/s1807-59322010000900005
Desaturation - distance ratio: a new concept for a functional assessment of interstitial lung diseases
Abstract
Introduction: The functional evaluation has become increasingly important in the understanding and management of patients with interstitial lung diseases. The cardiopulmonary exercise test and the six-minute walk test (6MWT), through their isolated variables, have been used to do this evaluation, with some limitations.
Objectives: We proposed a new composite index (desaturation distance ratio using continuous peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO₂) and the distance walked as a more reliable tool for doing a functional evaluation of these patients.
Methods: 6MWT was performed by interstitial lung diseases patients and controls. Analyzed parameters were walked distance and desaturation area (DAO₂), obtained by taking the difference between maximal SpO₂ possible (100%) and patient's SpO₂ every 2 seconds. desaturation distance ratio was calculated using the ratio between DAO₂ and distance walked.
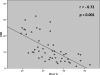
Results: Forty-nine interstitial lung diseases patients and 11 control subjects completed the protocol. The mean (SD) age was 60 (12) years and 65 (9) years, respectively (p:NS). Data obtained from 6MWT showed a significant statistical difference between interstitial lung diseases patients and controls: mean walked distance (430 and 602 meters, respectively); SpO₂ minimal maintained at least 10 seconds - SpO₂ min (85% and 94%, respectively), and median desaturation distance ratio (10 and 2.5, respectively). A correlation analysis, considering interstitial lung diseases patients, revealed the best correlation between desaturation distance ratio and DLco (r= - 0.72; p<0.001), being the correlation between SpO₂ min and DLco of 0.61 (p<0.001) and among walked distance and DLco of 0.58 (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Desaturation distance ratio is a promising concept and a more reliable physiologic tool to assess pulmonary diseases characterized by involvement of the alveolar-capillary membrane, such as interstitial lung diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Gascon M, Sanchez A, Gallego B, Celli BR. Inspiratory capacity, dynamic hyperinflation, breathlessness, and exercise performance during the 6‐minute‐walk test in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1395–9. - PubMed
-
- Chetta A, Aiello M, Foresi A, Marangio E, D'Ippolito R, Castagnaro A, et al. Relationship between outcome measures of six‐minute walk test and baseline lung function in patients with interstitial lung disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2001;18:170–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

