Unilateral or bilateral V-Y fasciocutaneous flaps for the coverage of soft tissue defects following total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 21050437
- PMCID: PMC2988015
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-799X-5-82
Unilateral or bilateral V-Y fasciocutaneous flaps for the coverage of soft tissue defects following total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: Soft tissue necrosis following total knee arthroplasty (TKA) may be the cause of the devastating complication of deep infection. It necessitates an immediate operative intervention because it could potentially jeopardise the arthroplasty or even the limb.
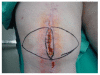
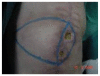
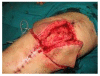
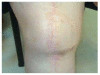
Methods: Sixteen consecutive patients with a mean age of 73,8 years (range 47 to76 years) over a 6-year period (January 2003 to December 2008) with wound dehiscence after TKA were enrolled in the present study. Unilateral or bilateral fasciocutaneous V-Y flaps that are differently oriented, depending on the local conditions of the tissues were used to reconstruct the soft tissues defects.
Results: In 15 of the 16 cases studied, the wound was successfully covered with the presented technique while in 1 patient a partial flap loss occurred, which was healed after surgical debridement and the application of vacuum system. No other complications occurred. Knee prosthesis was salvaged in all the patients with a good functional and esthetical outcome.
Conclusions: The presented reconstructive technique is a simple, quick, versatile and reliable solution for the coverage of soft tissue defects following TKA, more than 2 cm width and grade 1 and 2 according to Laing classification, provided the V-Y flaps are applied early in the postoperative period and no complex defects are involved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What Factors Influence the Success of Medial Gastrocnemius Flaps in the Treatment of Infected TKAs?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Mar;474(3):752-63. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4624-z. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26573319 Free PMC article.
-
V-Y fasciocutaneous advancement flap coverage of soft tissue defects of the foot in the patient at high risk.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010 Jan-Feb;49(1):71-4. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 Jun 30. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010. PMID: 20123292
-
Systematic Review and Comparative Meta-Analysis of Outcomes Following Pedicled Muscle versus Fasciocutaneous Flap Coverage for Complex Periprosthetic Wounds in Patients with Total Knee Arthroplasty.Arch Plast Surg. 2017 Mar;44(2):124-135. doi: 10.5999/aps.2017.44.2.124. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2017. PMID: 28352601 Free PMC article.
-
Wound complications in total knee arthroplasty. Which flap is to be used? With or without retention of prosthesis?Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011 Jul;19(7):1060-8. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1328-5. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. PMID: 21161178 Review.
-
Soft Tissue Reconstruction for Deep Defects over a Complicated Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review.J Knee Surg. 2020 Jul;33(7):732-744. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1684012. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Knee Surg. 2020. PMID: 30959536
Cited by
-
A combined debridement, antibiotics, and implant retention (DAIR) procedure with flap coverage for acute soft tissue defects following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study.J Bone Jt Infect. 2024 Oct 29;9(5):241-248. doi: 10.5194/jbji-9-241-2024. eCollection 2024. J Bone Jt Infect. 2024. PMID: 39539736 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of healing and complication rates between common flaps utilized in total knee arthroplasty: a review of the literature.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2022 Mar 26;34(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s43019-022-00145-3. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2022. PMID: 35346398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soft-tissue Defects After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Management and Reconstruction.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016 Nov;24(11):769-779. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00241. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016. PMID: 27673377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

