The tolerance of the nasal bone to blunt impact
- PMID: 21050587
- PMCID: PMC3242551
The tolerance of the nasal bone to blunt impact
Abstract
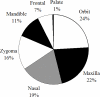
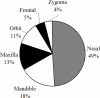
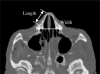
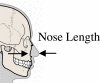
The nasal bone is among the most frequently broken facial bone due to all types of trauma and is the most frequently fractured facial bone due to motor vehicle collisions. This study reports the results of anterior-posterior impacts performed on male cadavers using a free-falling impactor with a flat impacting surface. The force at fracture onset was determined using an acoustic emission sensor. These non-censored data were utilized in parametric and non-parametric techniques to determine a relationship between applied force and fracture risk. Based on these analyses a 50% risk of fracture corresponded to an applied force of approximately 450 to 850 N. There was no correlation between fracture force and anthropometric measures of the nasal bone. Interestingly, age had a statistically significant relationship with the risk of nasal bone fracture. This study demonstrates the need for a non-censored measure of fracture occurrence when evaluating structures that can continue to support load after fracture onset.
Figures

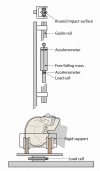





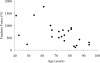
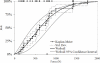


References
-
- Allison PD. Survival Analysis Using SAS: A Practical Guide Cary. SAS Press; 1995.
-
- Allsop D, Kennett K. Skull and Facial Bone Trauma. In: Nahum A, Melvin J, editors. Accidental Injury: Biomechanics and Prevention. 2nd Edition. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2002. pp. 254–76.
-
- Allsop D, Warner C, Wille M, Schneider D, Nahum A. Facial Impact Response – A Comparison of the Hybrid 3 Dummy and Human Cadaver. Society of Automotive Engineers. 1988 SAE 881719.
-
- Alvi A, Doherty T, Lewen G. Facial Fractures and Concomitant Injuries in Trauma Patients. The Laryngoscope. 2003;113 - PubMed
-
- Bermond F, Kallieris D, Mattern R, Ramet M, Bouquet R, Caire Y, Voiglio E. Human Face Response at an Angle to the Fore-aft Vertical Plane Impact. Proceedings of the IRCOBI. 1989:121–32.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
