Is off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting superior to conventional bypass in octogenarians?
- PMID: 21051050
- PMCID: PMC3071621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.09.012
Is off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting superior to conventional bypass in octogenarians?
Abstract
Objective: Selected patients appear to benefit from off-pump coronary artery bypass compared with conventional coronary artery bypass with cardiopulmonary bypass. It is unknown whether elderly patients undergoing isolated coronary artery bypass grafting operations derive any benefit when performed off-pump. We hypothesized that off-pump coronary bypass offers a greater operative benefit to elderly patients when compared with conventional coronary artery bypass.
Methods: A total of 1993 elderly patients (age ≥ 80 years) underwent isolated, primary coronary artery bypass graft operations at 16 different statewide centers from 2003 to 2008. Patients were stratified into 2 groups: conventional coronary artery bypass (n = 1589, age = 82.5 ± 2.4 years) and off-pump bypass (n = 404, age = 83.0 ± 2.4 years). Preoperative risk, intraoperative findings, postoperative complications, and costs were evaluated.
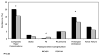
Results: Patients undergoing off-pump bypass grafting were marginally older (P = .001) and had higher rates of preoperative atrial fibrillation (14.6% vs 10.0%; P = .01) and New York Heart Association class IV heart failure (29.7% vs 21.1%; P < .001) than did those having conventional coronary bypass grafting. Other patient risk factors and operative variables, including Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted risk of mortality, were similar in both groups (P = .15). Compared with off-pump bypass, conventional coronary bypass incurred higher blood transfusion rates (2.0 ± 1.7 units vs 1.6 ± 1.9 units; P = .05) as well as more postoperative atrial fibrillation (28.4% vs 21.5%; P = .003), prolonged ventilation (14.7% vs 11.4%; P = .05), and major complications (20.1% vs 15.6%; P = .04). Importantly, postoperative stroke (2.6% vs 1.7%; P = .21), renal failure (8.1% vs 6.2%; P = .12), and postoperative length of stay (P = .41) were no different between groups. Despite more complications in patients having conventional bypass, operative mortality (P = .53) and hospital costs (P = .43) were similar to those of patients having off-pump procedures.
Conclusions: Performance of coronary artery bypass grafting among octogenarian patients is safe and effective. Off-pump coronary artery bypass confers shorter postoperative ventilation but equivalent mortality to conventional coronary artery bypass. Off-pump coronary artery bypass was associated with a reduction in the composite incidence of major complications in unadjusted and adjusted analyses and should be considered an acceptable alternative to conventional bypass for myocardial revascularization in elderly patients.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Mosby, Inc.
Figures
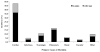
Comment in
-
Surgery: Off-pump CABG surgery safe and effective in the elderly.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011 Mar;8(3):124. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2011.4. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21475326 No abstract available.
References
-
- Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery Database. Executive Summary, 4th Harvest. 2009 Available at: http://www.sts.org/documents/pdf/ndb2010/20094thHarvestExecutiveSummary.pdf.
-
- Puskas JD, Thourani VH, Kilgo P, Cooper W, Vassiliades T, Vega JD, et al. Off-pump coronary artery bypass disproportionately benefits high-risk patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:1142–7. - PubMed
-
- Pierri MD, Capestro F, Zingaro C, Torracca L. The changing face of cardiac surgery patients: an insight into a Mediterranean region. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. Epub 2010 Apr 15. - PubMed
-
- Craver JM, Puskas JD, Weintraub WW, Shen Y, Guyton RA, Gott JP, et al. 601 octogenarians undergoing cardiac surgery: outcome and comparison with younger age groups. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;67:1104–10. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson TB, Jr, Coombs LP, Peterson ED. Internal thoracic artery grafting in the elderly patient undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: room for process improvement? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;123:869–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

