Long-term effects of epoprostenol on the pulmonary vasculature in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 21051399
- PMCID: PMC2972625
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.09-2815
Long-term effects of epoprostenol on the pulmonary vasculature in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
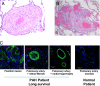
The current treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) uses vasodilator drugs. Although they improve symptoms associated with PAH, their chronic effects on the pulmonary vasculature and the right ventricle (RV) in humans remain unknown. We report the autopsy findings from a patient with idiopathic PAH treated with epoprostenol successfully for 18 years. The patient died of colon cancer. The pulmonary vasculature surprisingly showed extensive changes of a proliferative vasculopathy. Immunohistochemical studies confirmed ongoing cellular proliferation. Studies of the RV demonstrated concentric hypertrophy with seemingly preserved contractility. The myocardium shifted to glycolytic metabolism. Although the long-term use of epoprostenol contributed to the patient's increased survival, it did not prevent progression of the underlying vascular disease. Remarkably, the RV was able to sustain a normal cardiac output in the face of advanced vascular pathology. The mechanisms by which the RV adapts to chronic PAH need further study.
Figures

References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simonneau G. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(14):1425–1436. - PubMed
-
- Cowan KN, Heilbut A, Humpl T, Lam C, Ito S, Rabinovitch M. Complete reversal of fatal pulmonary hypertension in rats by a serine elastase inhibitor. Nat Med. 2000;6(6):698–702. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Long WA, et al. The Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(5):296–302. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin VV, Shillington A, Rich S. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension: the impact of epoprostenol therapy. Circulation. 2002;106(12):1477–1482. - PubMed
-
- Shah SJ, Thenappan T, Sur J, Rich S, Archer SL, Gomberg-Maitland M. Value of exercise treadmill testing in the risk stratification of patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circ Heart Fail. 2009;2(4):278–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

