Plastids contain a second sec translocase system with essential functions
- PMID: 21051552
- PMCID: PMC3075773
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.166546
Plastids contain a second sec translocase system with essential functions
Abstract
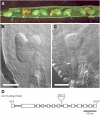
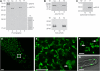
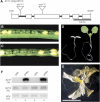
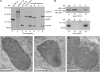
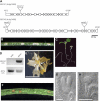
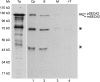
Proteins that are synthesized on cytoplasmic ribosomes but function within plastids must be imported and then targeted to one of six plastid locations. Although multiple systems that target proteins to the thylakoid membranes or thylakoid lumen have been identified, a system that can direct the integration of inner envelope membrane proteins from the stroma has not been previously described. Genetics and localization studies were used to show that plastids contain two different Sec systems with distinct functions. Loss-of-function mutations in components of the previously described thylakoid-localized Sec system, designated as SCY1 (At2g18710), SECA1 (At4g01800), and SECE1 (At4g14870) in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), result in albino seedlings and sucrose-dependent heterotrophic growth. Loss-of-function mutations in components of the second Sec system, designated as SCY2 (At2g31530) and SECA2 (At1g21650) in Arabidopsis, result in arrest at the globular stage and embryo lethality. Promoter-swap experiments provided evidence that SCY1 and SCY2 are functionally nonredundant and perform different roles in the cell. Finally, chloroplast import and fractionation assays and immunogold localization of SCY2-green fluorescent protein fusion proteins in root tissues indicated that SCY2 is part of an envelope-localized Sec system. Our data suggest that SCY2 and SECA2 function in Sec-mediated integration and translocation processes at the inner envelope membrane.
Figures


References
-
- Adamczyk BJ, Lehti-Shiu MD, Fernandez DE. (2007) The MADS domain factors AGL15 and AGL18 act redundantly as repressors of the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 50: 1007–1019 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Benz M, Bals T, Gügel IL, Piotrowski M, Kuhn A, Schünemann D, Soll J, Ankele E. (2009) Alb4 of Arabidopsis promotes assembly and stabilization of a non chlorophyll-binding photosynthetic complex, the CF1CF0-ATP synthase. Mol Plant 2: 1410–1424 - PubMed
-
- Berghöfer J, Karnauchov I, Herrmann RG, Klösgen RB. (1995) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the SecA protein from spinach chloroplasts: evidence for azide resistance of Sec-dependent protein translocation across thylakoid membranes in spinach. J Biol Chem 270: 18341–18346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

