Switching from calcineurin inhibitor-based regimens to a belatacept-based regimen in renal transplant recipients: a randomized phase II study
- PMID: 21051752
- PMCID: PMC3052236
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05840710
Switching from calcineurin inhibitor-based regimens to a belatacept-based regimen in renal transplant recipients: a randomized phase II study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Prolonged use of calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) in kidney transplant recipients is associated with renal and nonrenal toxicity and an increase in cardiovascular risk factors. Belatacept-based regimens may provide a treatment option for patients who switch from CNI-based maintenance immunosuppression.
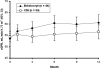
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This is a randomized, open-label Phase II trial in renal transplant patients with stable graft function and receiving a CNI-based regimen. Patients who were ≥6 months but ≤36 months after transplantation were randomized to either switch to belatacept or continue CNI treatment. All patients received background maintenance immunosuppression. The primary end point was the change in calculated GFR (cGFR) from baseline to month 12.
Results: Patients were randomized either to switch to belatacept (n=84) or to remain on a CNI-based regimen (n=89). At month 12, the mean (SD) change from baseline in cGFR was higher in the belatacept group versus the CNI group. Six patients in the belatacept group had acute rejection episodes, all within the first 6 months; all resolved with no allograft loss. By month 12, one patient in the CNI group died with a functioning graft, whereas no patients in the belatacept group had graft loss. The overall safety profile was similar between groups.
Conclusions: The study identifies a potentially safe and feasible method for switching stable renal transplant patients from a cyclosporine- or tacrolimus-based regimen to a belatacept-based regimen, which may allow improved renal function in patients currently treated with CNIs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00402168.
Figures
References
-
- Meier-Kriesche HU, Schold JD, Srinivas TR, Kaplan B: Lack of improvement in renal allograft survival despite a marked decrease in acute rejection rates over the most recent era. Am J Transplant 4: 378–383, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Naesens M, Kuypers DR, Sarwal M: Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4: 481–508, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O'Connell PJ, Allen RD, Chapman JR: The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N Engl J Med 349: 2326–2333, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Ducloux D, Motte G, Kribs M, Abdelfatah AB, Bresson-Vautrin C, Rebibou JM, Chalopin JM: Hypertension in renal transplantation: Donor and recipient risk factors. Clin Nephrol 57: 409–413, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Mathis AS, Dave N, Knipp GT, Friedman GS: Drug-related dyslipidemia after renal transplantation. Am J Health Syst Pharm 61: 565–585, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical