The Cain and Abl of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and transforming growth factor-β in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 21051857
- PMCID: PMC3245834
- DOI: 10.1159/000320163
The Cain and Abl of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and transforming growth factor-β in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
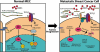
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) normally inhibits breast cancer development by preventing mammary epithelial cell (MEC) proliferation, by inducing MEC apoptosis, and by creating cell microenvironments that maintain MEC homeostasis and prevent their uncontrolled growth and motility. Mammary tumorigenesis elicits dramatic alterations in MEC architecture and microenvironment integrity, which collectively counteract the tumor-suppressing activities of TGF-β and enable its stimulation of breast cancer invasion and metastasis. How malignant MECs overcome the cytostatic actions imposed by normal microenvironments and TGF-β, and how abnormal microenvironments conspire with TGF-β to stimulate the development and progression of mammary tumors remains largely undefined. These knowledge gaps have prevented science and medicine from implementing treatments effective in simultaneously targeting abnormal cellular microenvironments, and in antagonizing the oncogenic activities of TGF-β in developing and progressing breast cancers. c-Abl is a ubiquitously expressed nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinase that essentially oversees all aspects of cell physiology, including the regulation of cell proliferation, migration and adhesion, as well as that of cell survival. Thus, the biological functions of c-Abl are highly reminiscent of those attributed to TGF-β, including the ability to function as either a suppressor or promoter of tumorigenesis. Interestingly, while dysregulated Abl activity clearly promotes tumorigenesis in hematopoietic cells, an analogous role for c-Abl in regulating solid tumor development, including those of the breast, remains controversial. Here, we review the functions of c-Abl in regulating breast cancer development and progression, and in alleviating the oncogenic activities of TGF-β and its stimulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition during mammary tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
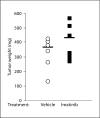
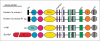
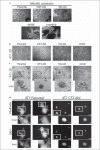
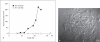
References
-
- Agami R., Blandino G., Oren M., Shaul Y. Interaction of c-Abl and p73alpha and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature. 1999;399:809–813. - PubMed
-
- Bakin A.V., Tomlinson A.K., Bhowmick N.A., Moses H.L., Arteaga C.L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for TGF-β-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36803–36810. - PubMed
-
- Baskaran R., Wood L.D., Whitaker L.L., Canman C.E., Morgan S.E., Xu Y., Barlow C., Baltimore D., Wynshaw-Boris A., Kastan M.B., Wang J.Y. Ataxia telangiectasia mutant protein activates c-Abl tyrosine kinase in response to ionizing radiation. Nature. 1997;387:516–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

