RIN4-like proteins mediate resistance protein-derived soybean defense against Pseudomonas syringae
- PMID: 21051954
- PMCID: PMC3115253
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.5.11.13462
RIN4-like proteins mediate resistance protein-derived soybean defense against Pseudomonas syringae
Abstract
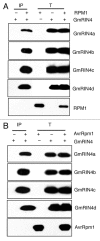
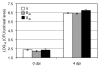
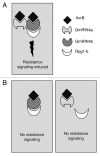
Resistance (R) protein mediated recognition of pathogen avirulence effectors triggers signaling that induces a very robust form of species-specific immunity in plants. The soybean Rpg1-b protein mediates this form of resistance against the bacterial blight pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae expressing AvrB Pgyrace4. Likewise, the Arabidopsis RPM1 protein also mediates species-specific resistance against AvrB expressing bacteria. RPM1 and Rpg1-b are non-orthologous and differ in their requirements for downstream signaling components. We recently showed that the activation of Rpg1-b derived resistance signaling requires two host proteins that directly interact with AvrB. These proteins share high sequence similarity with the Arabidopsis RPM1 interacting protein 4 (RIN4), which is essential for RPM1-derived resistance. The two soybean RIN4-like proteins (GmRIN4a and b) differ in their abilities to interact with Rpg1-b as well as to complement the Arabidopsis rin4 mutation. Because the two GmRIN4 proteins interact with each other, we proposed that they might function as a heteromeric complex in mediating Rpg1-b-derived resistance. Absence of GmRIN4a or b enhanced basal resistance against bacterial and oomycete pathogens in soybean. Lack of GmRIN4a also enhanced the virulence of avrB bacteria in plants lacking Rpg1-b. Our studies suggest that multiple RIN4-like proteins proteins mediate R-mediated signaling, in soybean.
Figures

Comment on
-
RPG1-B-derived resistance to AvrB-expressing Pseudomonas syringae requires RIN4-like proteins in soybean.Plant Physiol. 2010 Jul;153(3):1199-211. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158147. Epub 2010 May 18. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20484023 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
RPG1-B-derived resistance to AvrB-expressing Pseudomonas syringae requires RIN4-like proteins in soybean.Plant Physiol. 2010 Jul;153(3):1199-211. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158147. Epub 2010 May 18. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20484023 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas syringae Effector AvrPphB Suppresses AvrB-Induced Activation of RPM1 but Not AvrRpm1-Induced Activation.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015 Jun;28(6):727-35. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-08-14-0248-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015. PMID: 25625821
-
RIN4 interacts with Pseudomonas syringae type III effector molecules and is required for RPM1-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis.Cell. 2002 Mar 22;108(6):743-54. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00661-x. Cell. 2002. PMID: 11955429
-
Plant defense: one post, multiple guards?!Mol Cell. 2003 Feb;11(2):284-6. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00072-8. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12620215 Review.
-
Role of RIN4 in Regulating PAMP-Triggered Immunity and Effector-Triggered Immunity: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Mol Cells. 2019 Jul 31;42(7):503-511. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2019.2433. Mol Cells. 2019. PMID: 31362467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissection of Resistance Genes to Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola in UI3 Common Bean Cultivar.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 23;18(12):2503. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122503. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29168746 Free PMC article.
-
The Upregulated Expression of the Citrus RIN4 Gene in HLB Diseased Citrus Aids Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):6971. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136971. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805971 Free PMC article.
-
RIN4 recruits the exocyst subunit EXO70B1 to the plasma membrane.J Exp Bot. 2017 Jun 1;68(12):3253-3265. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx007. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28338727 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory Peptides as Bullets: Effector Peptides from Pathogens against Antimicrobial Peptides from Soybean.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 5;21(23):9294. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239294. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcriptional response to the olive fruit fly (Bactrocera oleae) reveals extended differences between tolerant and susceptible olive (Olea europaea L.) varieties.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 10;12(8):e0183050. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183050. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28797083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scofield SR, Tobias CM, Rathjen JP, Chang JH, Lavelle DT, Michelmore RW, et al. Molecular basis of gene-for-gene specificity in bacterial speck disease of tomato. Science. 1996;274:2063–2065. - PubMed
-
- Leister RT, Katagiri F. A resistance gene product of the nucleotide binding site—leucine rich repeats class can form a complex with bacterial avirulence proteins in vivo. Plant J. 2000;22:345–354. - PubMed
-
- Van der Biezen EA, Jones JDG. Plant disease-resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends Plant Sci. 1998;23:454–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
