Effect of acetaminophen (paracetamol) on human osteosarcoma cell line MG63
- PMID: 21052086
- PMCID: PMC4003333
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.129
Effect of acetaminophen (paracetamol) on human osteosarcoma cell line MG63
Abstract
Aim: To examine the effects of acetaminophen (paracetamol), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), on different cellular and functional parameters of the human osteosarcoma cell line MG63.
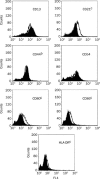
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to study proliferation, antigenic profile, and phagocytic activity, and radioimmunoassay was used to determine osteocalcin synthesis as a cell differentiation marker.
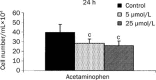
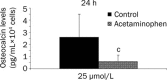
Results: Short-term treatment with therapeutic doses of paracetamol(5 or 25 μmol/L) reduced cell proliferation, osteocalcin synthesis, and phagocyte activity, and increased the expression of antigens involved in antigen presentation to T lymphocytes (CD80, CD86, HLA-DR).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that paracetamol activates the osteoblast, inducing its immunogenic action to the detriment of its bone formation capacity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of ibuprofen on proliferation, differentiation, antigenic expression, and phagocytic capacity of osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Metab. 2012 Sep;30(5):554-60. doi: 10.1007/s00774-012-0356-2. Epub 2012 Apr 28. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012. PMID: 22543821
-
Therapeutic doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit osteosarcoma MG-63 osteoblast-like cells maturation, viability, and biomineralization potential.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Sep 19;2013:809891. doi: 10.1155/2013/809891. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24170983 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of molecules involved in antigen presentation and T cell activation (HLA-DR, CD80, CD86, CD44 and CD54) by cultured human osteoblasts.J Periodontol. 2000 Apr;71(4):614-7. doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.4.614. J Periodontol. 2000. PMID: 10807126
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing the Efficacy of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs, Opioids, and Paracetamol in the Treatment of Acute Renal Colic.Eur Urol. 2018 Apr;73(4):583-595. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29174580
-
Repercussions of NSAIDS drugs on bone tissue: the osteoblast.Life Sci. 2015 Feb 15;123:72-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25625244 Review.
Cited by
-
Repercussion of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the gene expression of human osteoblasts.PeerJ. 2018 Aug 14;6:e5415. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5415. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 30128197 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of NSAIDs on pre-osteoblast viability and osteogenic differentiation.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):740. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10172. Epub 2021 May 10. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34046094 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of aspirin on cell growth of human MG-63 osteosarcoma line.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:834246. doi: 10.1100/2012/834246. Epub 2012 May 2. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22654634 Free PMC article.
-
Acetaminophen Interactions with Phospholipid Vesicles Induced Changes in Morphology and Lipid Dynamics.Langmuir. 2021 Aug 10;37(31):9560-9570. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01458. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Langmuir. 2021. PMID: 34328747 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ibuprofen on proliferation, differentiation, antigenic expression, and phagocytic capacity of osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Metab. 2012 Sep;30(5):554-60. doi: 10.1007/s00774-012-0356-2. Epub 2012 Apr 28. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012. PMID: 22543821
References
-
- Ferreira SH, Nakamura M, Castro M. The hyperalgesic effects of prostaciclin and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins. 1978;16:31–7. - PubMed
-
- Smith WL, Dewitt DL, Garavito RM. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Ann Rev Biochem. 2000;69:145–82. - PubMed
-
- Esplugues JV, Barrachina MD.Mediadores celulares II. Eicosanoides Óxido Nítrico y factor activador de plaquetasIn: Flórez J, Armijo JA, Mediavilla A, editors. Farmacología Humana. Barcelona: Masson; 2004p47–362.
-
- Hinz B, Cheremina O, Brunek Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxigenase-2 inhibitor in man. FASEB J. 2008;22:383–90. - PubMed
-
- Davies M, Anderson K. Clinical pharmacokinetic of diclofenac: therapeutic insights and pitfalls. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997;33:184–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

