Modulation of gene expression in endothelial cells by hyperlipaemic postprandial serum from healthy volunteers
- PMID: 21052530
- PMCID: PMC2935529
- DOI: 10.1007/s12263-010-0166-x
Modulation of gene expression in endothelial cells by hyperlipaemic postprandial serum from healthy volunteers
Abstract
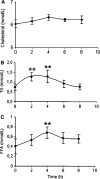
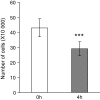
A single high-fat challenge induces plasmatic pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidative responses in the postprandial state, even in healthy men. This period is also associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction, which is an early event in the development of cardiovascular diseases. However, knowledge about the mechanisms involved in postprandial hyperlipaemia-induced endothelial dysfunction is sparse. An objective of our study was to characterize the behaviour and gene expression of vascular endothelial cells exposed to postprandial hyperlipaemic sera. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured in media containing 10% serum from healthy men withdrawn either before or 4 h after a high-fat challenge. Endothelial cell proliferation, adhesion and migration were then assessed. The transcriptomic profiles of endothelial cells exposed to pre and postprandial sera were also compared. Exposure to postprandial hyperlipaemic sera significantly decreased HUVEC proliferation when compared to preprandial serum (P < 0.0001), while no changes in migration or endothelial/monocyte interactions were observed. The transcriptomic analysis revealed changes in the expression of 675 genes, of which 431 have a known function. Among them, a set of differentially expressed genes was linked to cell cycle regulation and apoptosis and are regulated in favour of cell cycle arrest or death. This result was confirmed by measuring the induction of apoptosis after postprandial sera exposure (P = 0.011). Taken together, the transcriptomic results and pathway analysis showed that postprandial serum promotes apoptosis in HUVECs, potentially through the activation of the p53 network. We conclude that upon postprandial serum exposure, vascular endothelial cells transcriptionally regulate genes involved in the control of cell cycle and death to favour growth arrest and apoptosis. These findings support the hypothesis that postprandial hyperlipaemia is associated with vascular dysfunction and offer new insights into the mechanisms involved.
Electronic supplementary material: The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s12263-010-0166-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Apoptosis atherogenesis; Nutrigenomics; Postprandial hyperlipaemia; Vascular endothelial cells.
Figures
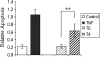
Similar articles
-
Gene Expression, Oxidative Stress, and Senescence of Primary Coronary Endothelial Cells Exposed to Postprandial Serum of Healthy Adult and Elderly Volunteers after Oven-Cooked Meat Meals.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3868545. doi: 10.1155/2017/3868545. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29379227 Free PMC article.
-
Postprandial serum induces apoptosis in endothelial cells: Role of polymorphonuclear-derived myeloperoxidase and metalloproteinase-9 activity.Atherosclerosis. 2008 Jun;198(2):458-67. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.11.030. Epub 2008 Jan 4. Atherosclerosis. 2008. PMID: 18177875
-
Single Triglyceride-Rich Meal Destabilizes Barrier Functions and Initiates Inflammatory Processes of Endothelial Cells.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020 Jan;40(1):43-53. doi: 10.1089/jir.2018.0173. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020. PMID: 31460824
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
Postprandial triglycerides and endothelial function.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109(4):S533-47. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-15116. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11453041 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying some major common risk factors of stroke.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 18;8(8):e10218. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10218. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36060992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Expression, Oxidative Stress, and Senescence of Primary Coronary Endothelial Cells Exposed to Postprandial Serum of Healthy Adult and Elderly Volunteers after Oven-Cooked Meat Meals.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3868545. doi: 10.1155/2017/3868545. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29379227 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based clustering of multi-tissue gene expression data.Bioinformatics. 2020 Mar 1;36(6):1807-1813. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz805. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31688915 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis Induced by Postprandial Lipemia.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Apr 29;8:636947. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.636947. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33996937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borlado LR, Mendez J (2007) CDC6: from DNA replication to cell cycle checkpoints and oncogenesis. Carcinogenesis, 28 Nov - PubMed
-
- Brizzi MF, Garbarino G, Rossi PR, Pagliardi GL, Arduino C, Avanzi GC, Pegoraro L. Interleukin 3 stimulates proliferation and triggers endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 gene activation of human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1993;91(6):2887–2892. doi: 10.1172/JCI116534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
