Targeted Therapy of Ewing's Sarcoma
- PMID: 21052545
- PMCID: PMC2968715
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/686985
Targeted Therapy of Ewing's Sarcoma
Abstract
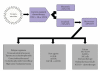
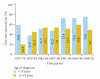
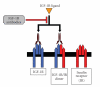
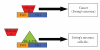
Refractory and/or recurrent Ewing's sarcoma (EWS) remains a clinical challenge because the disease's resistance to therapy makes it difficult to achieve durable results with standard treatments that include chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. Recently, insulin-like-growth-factor-1-receptor (IGF1R) antibodies have been shown to have a modest single-agent activity in EWS. Patient selection using biomarkers and understanding response and resistance mechanisms in relation to IGF1R and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways are areas of active research. Since EWS has a unique tumor-specific EWS-FLI1 t(11;22) translocation and oncogenic fusion protein, inhibition of EWS-FLI1 transcription, translation, and/or protein function may be key to eradicating EWS at the stem-cell level. Recently, a small molecule that blocks the protein-protein interaction of EWS-FLI1 with RNA helicase A has been shown in preclinical models to inhibit EWS growth. The successful application of this first-in-class protein-protein inhibitor in the clinic could become a model system for translocation-associated cancers such as EWS.
Figures
References
-
- Cotterill SJ, Ahrens S, Paulussen M, et al. Prognostic factors in Ewing’s tumor of bone: analysis of 975 patients from the European Intergroup Cooperative Ewing’s Sarcoma Study Group. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;18(17):3108–3114. - PubMed
-
- Burdach S, Jürgens H. High-dose chemoradiotherapy (HDC) in the Ewing family of tumors (EFT) Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2002;41(2):169–189. - PubMed
-
- Ladenstein R, Pötschger U, Le Deley MC, et al. Primary disseminated multifocal Ewing sarcoma: results of the Euro-EWING 99 trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2009;28:2022–9864. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

