Chromogranin/secretogranin proteins in murine heart: myocardial production of chromogranin A fragment catestatin (Chga(364-384))
- PMID: 21052719
- PMCID: PMC2996542
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-010-1059-4
Chromogranin/secretogranin proteins in murine heart: myocardial production of chromogranin A fragment catestatin (Chga(364-384))
Abstract
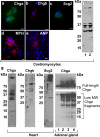
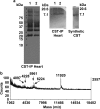
In the heart, the secretory granules containing the atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP) and B-type myocardial natriuretic peptide (BNP) provide the basis for the endocrine function of this organ. We sought to determine whether atrial and myocardial secretory granules contain chromogranin/secretogranin proteins including chromogranin A (CHGA/Chga), chromogranin B (CHGB/Chgb) and secretogranin II (SCG2/Scg2). Deconvolution microscopy on immunolabeled proteins revealed the presence of Chga, Chgb, and Scg2 in murine cardiac secretory granules. The presence of low plasma catestatin (CST: mChga(364-384)) in older mice indicates diminished processing of Chga to CST with advancement of age, which is comparable to that found in humans. We have previously shown that CST (hCHGA(352-372)) exerts potent cardio-suppressive effects on frog and rat heart, but the source of CST for such action has remained elusive. In the present study, we found CST-related peptides in cardiomyocytes and in heart, which establishes an autocrine/paracrine function of CST in cardiac tissue. We conclude that cardiac secretory granules contain Chga, Chgb and Scg2 and that Chga is processed to CST in murine heart.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Chromogranin A: immunocytochemical localization in secretory granules of frog atrial cardiomyocytes].Tsitologiia. 2007;49(7):538-43. Tsitologiia. 2007. PMID: 17918337 Russian.
-
The importance of chromogranin A in the development and function of endocrine pancreas.Regul Pept. 2008 Nov 29;151(1-3):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2008.07.005. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Regul Pept. 2008. PMID: 18722481
-
The neuroendocrine peptide catestatin is a cutaneous antimicrobial and induced in the skin after injury.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Jun;128(6):1525-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701225. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18185531 Free PMC article.
-
Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A.Regul Pept. 2010 Jun 8;162(1-3):33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Regul Pept. 2010. PMID: 20116404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranin A-derived peptides pancreastatin and catestatin: emerging therapeutic target for diabetes.Amino Acids. 2023 May;55(5):549-561. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03252-x. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 36914766 Review.
Cited by
-
The novel chromogranin A-derived serpinin and pyroglutaminated serpinin peptides are positive cardiac β-adrenergic-like inotropes.FASEB J. 2012 Jul;26(7):2888-98. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-201111. Epub 2012 Mar 29. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22459152 Free PMC article.
-
Catestatin and Advanced Glycation End-Products: Potential Indicators of Cardiovascular Risk in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 23;15(2):169. doi: 10.3390/biom15020169. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001472 Free PMC article.
-
Catestatin as a New Prognostic Marker in Stable Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Two-Year Follow-Up.Dis Markers. 2020 Oct 1;2020:8847211. doi: 10.1155/2020/8847211. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33082887 Free PMC article.
-
Catestatin increases the expression of anti-apoptotic and pro-angiogenetic factors in the post-ischemic hypertrophied heart of SHR.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 6;9(8):e102536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102536. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0246900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246900. PMID: 25099124 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A novel catestatin-induced antiadrenergic mechanism triggered by the endothelial PI3K-eNOS pathway in the myocardium.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Sep 1;91(4):617-24. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr129. Epub 2011 May 4. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21543385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelone T, Quintieri AM, Brar BK, Limchaiyawat PT, Tota B, Mahata SK, Cerra MC. The antihypertensive chromogranin A peptide catestatin acts as a novel endocrine/paracrine modulator of cardiac inotropism and lusitropism. Endocrinology. 2008;149:4780–4793. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0318. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Mahata M, Das M, Gayen JR, Taupenot L, Torpey JW, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK. Proteolytic cleavage of human chromogranin A containing naturally occurring catestatin variants: differential processing at catestatin region by plasmin. Endocrinology. 2008;149:749–757. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0838. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswas N, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Courel M, Gayen JR, Vaingankar SM, Mahata M, Torpey JW, Taupenot L, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK. Cathepsin L Co-localizes with chromogranin A in chromaffin vesicles to generate active peptides. Endocrinology. 2009;150:3547–3557. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1613. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

