Neuropsychopharmacological understanding for therapeutic application of morphinans
- PMID: 21052935
- PMCID: PMC3399693
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-010-1009-4
Neuropsychopharmacological understanding for therapeutic application of morphinans
Abstract
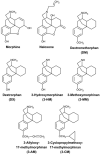
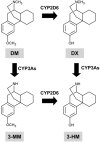
Morphinans are a class of compounds containing the basic structure of morphine. It is well-known that morphinans possess diverse pharmacological effects on the central nervous system. This review will demonstrate novel neuroprotective effects of several morphinans such as, dextromethorphan, its analogs and naloxone on the models of multiple neurodegenerative disease by modulating glial activation associated with the production of a host of proinflammatory and neurotoxic factors, although dextromethorphan possesses neuropsychotoxic potentials. The neuroprotective effects and the therapeutic potential for the treatment of excitotoxic and inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases, and underlying mechanism of morphinans are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Aram JA, Martin D, Tomczyk M, Zeman S, Millar J, Pohler G, Lodge D. Neocortical epileptogenesis in vitro: studies with N-methyl-D-aspartate, phencyclidine, sigma and dextromethorphan receptor ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989;248:320–328. - PubMed
-
- Bem JL, Peck R. Dextromethorphan. An overview of safety issues. Drug Saf. 1992;7:190–199. - PubMed
-
- Bokesch PM, Marchand JE, Connelly CS, Wurm WH, Kream RM. Dextromethorphan inhibits ischemia-induced c-fos expression and delayed neuronal death in hippocampal neurons. Anesthesiology. 1994;81:470–477. - PubMed
-
- Britton P, Lu XC, Laskosky MS, Tortella FC. Dextromethorphan protects against cerebral injury following transient, but not permanent, focal ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 1997;60:1729–1740. - PubMed
-
- Carliss RD, Radovsky A, Chengelis CP, O’neill TP, Shuey DL. Oral administration of dextromethorphan does not produce neuronal vacuolation in the rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 2007;28:813–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical