Endocrine disrupting chemicals targeting estrogen receptor signaling: identification and mechanisms of action
- PMID: 21053929
- PMCID: PMC3119362
- DOI: 10.1021/tx100231n
Endocrine disrupting chemicals targeting estrogen receptor signaling: identification and mechanisms of action
Abstract
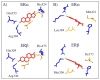
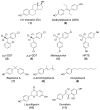
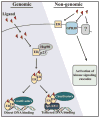
Many endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) adversely impact estrogen signaling by interacting with two estrogen receptors (ERs): ERα and ERβ. Though the receptors have similar ligand binding and DNA binding domains, ERα and ERβ have some unique properties in terms of ligand selectivity and target gene regulation. EDCs that target ER signaling can modify genomic and nongenomic ER activity through direct interactions with ERs, indirectly through transcription factors such as the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), or through modulation of metabolic enzymes that are critical for normal estrogen synthesis and metabolism. Many EDCs act through multiple mechanisms as exemplified by chemicals that bind both AhR and ER, such as 3-methylcholanthrene. Other EDCs that target ER signaling include phytoestrogens, bisphenolics, and organochlorine pesticides, and many alter normal ER signaling through multiple mechanisms. EDCs can also display tissue-selective ER agonist and antagonist activities similar to selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) designed for pharmaceutical use. Thus, biological effects of EDCs need to be carefully interpreted because EDCs can act through complex tissue-selective modulation of ERs and other signaling pathways in vivo. Current requirements by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency require some in vitro and cell-based assays to identify EDCs that target ER signaling through direct and metabolic mechanisms. Additional assays may be useful screens for identifying EDCs that act through alternative mechanisms prior to further in vivo study.
Figures
References
-
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Endocrinology. 1997;138:863–870. - PubMed
-
- Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Grandien K, Lagercrantz S, Lagercrantz J, Fried G, Nordenskjold M, Gustafsson JA. Human estrogen receptor β-gene structure, chromosomal localization, and expression pattern. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:4258–4265. - PubMed
-
- Taylor AH, Al-Azzawi F. Immunolocalisation of oestrogen receptor beta in human tissues. J Mol Endocrinol. 2000;24:145–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

