Binding to and photo-oxidation of cardiolipin by the phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4
- PMID: 21054078
- PMCID: PMC2945736
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3484256
Binding to and photo-oxidation of cardiolipin by the phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4
Abstract
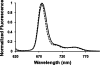
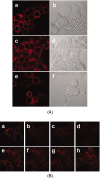
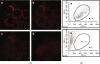
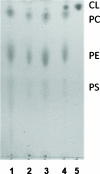
Cardiolipin is a unique phospholipid of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Its peroxidation correlates with release of cytochrome c and induction of apoptosis. The phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4 binds preferentially to the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Earlier Förster resonance energy transfer studies showed colocalization of Pc 4 and cardiolipin, which suggests cardiolipin as a target of photodynamic therapy (PDT) with Pc 4. Using liposomes as membrane models, we find that Pc 4 binds to cardiolipin-containing liposomes similarly to those that do not contain cardiolipin. Pc 4 binding is also studied in MCF-7c3 cells and those whose cardiolipin content was reduced by treatment with palmitate. Decreased levels of cardiolipin are quantified by thin-layer chromatography. The similar level of binding of Pc 4 to cells, irrespective of palmitate treatment, supports the lack of specificity of Pc 4 binding. Thus, factors other than cardiolipin are likely responsible for the preferential localization of Pc 4 in mitochondria. Nonetheless, cardiolipin within liposomes is readily oxidized by Pc 4 and light, yielding apparently mono- and dihydroperoxidized cardiolipin. If similar products result from exposure of cells to Pc 4-PDT, they could be part of the early events leading to apoptosis following Pc 4-PDT.
Figures

References
-
- MacDonald I. and Dougherty T. J., “Basic principles of photodynamic therapy,” J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 5, 105–129 (2001). 10.1002/jpp.328 - DOI
-
- Weishaupt K. R., Gomer C. J., and Dougherty T. J., “Identification of singlet oxygen as the cytotoxic agent in photoinactivation of a murine tumor,” Cancer Res. 36(7, Pt. 1), 2326–2329 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Buytaert E., Dewaele M., and Agostinis P., “Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy,” Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1776(1), 86–107 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

