An essential role for adenosine signaling in alcohol abuse
- PMID: 21054262
- PMCID: PMC3922619
- DOI: 10.2174/1874473711003030163
An essential role for adenosine signaling in alcohol abuse
Abstract
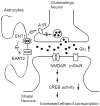
In the central nervous system (CNS), adenosine plays an important role in regulating neuronal activity and modulates signaling by other neurotransmitters, including GABA, glutamate, and dopamine. Adenosine suppresses neurotransmitter release, reduces neuronal excitability, and regulates ion channel function through activation of four classes of G protein-coupled receptors, A(1), A(2A), A(2B), and A(3). Central adenosine are largely controlled by nucleoside transporters, which transport adenosine levels across the plasma membrane. Adenosine has been shown to modulate cortical glutamate signaling and ventral-tegmental dopaminergic signaling, which are involved in several aspects of alcohol use disorders. Acute ethanol elevates extracellular adenosine levels by selectively inhibiting the type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter, ENT1. Raised adenosine levels mediate the ataxic and sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol through activation of A(1) receptors in the cerebellum, striatum, and cerebral cortex. Recently, we have shown that pharmacological inhibition or genetic deletion of ENT1 reduces the expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2), the primary regulator of extracellular glutamate, in astrocytes. These lines of evidence support a central role for adenosine-mediated glutamate signaling and the involvement of astrocytes in regulating ethanol intoxication and preference. In this paper, we discuss recent findings on the implication of adenosine signaling in alcohol use disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Burnstock G. Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:166–76. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:575–90. - PubMed
-
- Latini S, Pedata F. Adenosine in the central nervous system: release mechanisms and extracellular concentrations. J Neurochem. 2001;79:463–84. - PubMed
-
- Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA. The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:31–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
