Intrathecal orexin A increases sympathetic outflow and respiratory drive, enhances baroreflex sensitivity and blocks the somato-sympathetic reflex
- PMID: 21054340
- PMCID: PMC3042205
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01102.x
Intrathecal orexin A increases sympathetic outflow and respiratory drive, enhances baroreflex sensitivity and blocks the somato-sympathetic reflex
Abstract
Background: Intrathecal (i.t.) injection of orexin A (OX-A) increases blood pressure and heart rate (HR), but the effects of OX-A on sympathetic and phrenic, nerve activity, and the baroreflex(es), somato-sympathetic and hypoxic chemoreflex(es) are unknown.
Experimental approach: Urethane-anaesthetized, vagotomized and artificially ventilated male Sprague-Dawley rats were examined in this study. The effects of i.t. OX-A (20 nmol 10 µL⁻¹) on cardiorespiratory parameters, and responses to stimulation of the sciatic nerve (electrical), arterial baroreceptors (phenylephrine hydrochloride, 0.01 mg kg⁻¹ i.v.) and peripheral (hypoxia) chemoreceptors were also investigated.
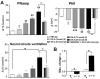
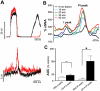
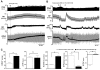
Key results: i.t. OX-A caused a prolonged dose-dependent sympathoexcitation, pressor response and tachycardia. The peak effect was observed at 20 nmol with increases in mean arterial pressure, HR and splanchnic sympathetic nerve activity (sSNA) of 32 mmHg, 52 beats per minute and 100% from baseline respectively. OX-A also dose-dependently increased respiratory drive, as indicated by a rise in phrenic nerve amplitude and a fall in phrenic nerve frequency, an increase in neural minute ventilation, a lengthening of the expiratory period, and a shortening of the inspiratory period. All effects of OX-A (20 nmol) were attenuated by the orexin receptor 1 antagonist SB 334867. OX-A significantly reduced both sympathoexcitatory peaks of somato-sympathetic reflex while increasing baroreflex sensitivity. OX-A increased the amplitude of the pressor response and markedly amplified the effect of hypoxia on sSNA.
Conclusions: Thus, activation of OX receptors in rat spinal cord alters cardiorespiratory function and differentially modulates sympathetic reflexes.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

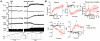
Similar articles
-
Orexin A in rat rostral ventrolateral medulla is pressor, sympatho-excitatory, increases barosensitivity and attenuates the somato-sympathetic reflex.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(7):2292-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01694.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21951179 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal neuromedin U induces biphasic effects on sympathetic vasomotor tone, increases respiratory drive and attenuates sympathetic reflexes in rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):617-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01436.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21488865 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cardiorespiratory and sympathetic reflex responses to microinjection of neuromedin U in rat rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Apr;341(1):213-24. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.191254. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22262923
-
[Central action of orexins on sympathetic outflow and cardiovascular function with a focus on the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus].Masui. 2007 Jan;56(1):30-9. Masui. 2007. PMID: 17243643 Review. Japanese.
-
Cardiorespiratory coupling: common rhythms in cardiac, sympathetic, and respiratory activities.Prog Brain Res. 2014;209:191-205. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63274-6.00010-2. Prog Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24746049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exaggerated postnatal surge of orexin neurons and the effects of elimination of excess orexin on blood pressure and exaggerated chemoreflex in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Front Physiol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1341649. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1341649. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39469444 Free PMC article.
-
Role of orexin in modulating arousal, feeding, and motivation.Front Behav Neurosci. 2013 Apr 18;7:28. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00028. eCollection 2013. Front Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23616752 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Role of CRF-Hcrt Interaction in the Infralimbic Cortex in the Emergence and Maintenance of Compulsive Alcohol-Seeking Behavior.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Feb;44(2):354-367. doi: 10.1111/acer.14264. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31840823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrathecal neurotensin is hypotensive, sympathoinhibitory and enhances the baroreflex in anaesthetized rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):378-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01760.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22035146 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin A in rat rostral ventrolateral medulla is pressor, sympatho-excitatory, increases barosensitivity and attenuates the somato-sympathetic reflex.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(7):2292-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01694.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21951179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antunes VR, Cristina Brailoiu G, Kwok EH, Scruggs P, Dun ANJ. Orexins/hypocretins excite rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. 2001;281:R1801–R1807. - PubMed
-
- Bingham S, Davey PT, Babbs AJ, Irving EA, Sammons MJ, Wyles M, et al. Orexin-A, an hypothalamic peptide with analgesic properties. Pain. 2001;92:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Burke PG, Li Q, Costin ML, McMullan S, Pilowsky PM, Goodchild AK. Somatostatin 2A receptor-expressing presympathetic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla maintain blood pressure. Hypertension. 2008;52:1127–1133. - PubMed
-
- Chen CT, Hwang LL, Chang JK, Dun NJ. Pressor effects of orexins injected intracisternally and to rostral ventrolateral medulla of anesthetized rats. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:R692–R697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

