Impact of food restriction and cocaine on locomotion in ghrelin- and ghrelin-receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 21054685
- PMCID: PMC3354738
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00253.x
Impact of food restriction and cocaine on locomotion in ghrelin- and ghrelin-receptor knockout mice
Abstract
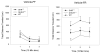
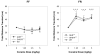
Food restriction (FR) augments the behavioral and reinforcing effects of psychomotor stimulants such as cocaine or amphetamine; effects that may be related to the capacity of FR to increase plasma levels of ghrelin (GHR), a 28-amino acid orexigenenic peptide linked to activation of brain dopamine systems. The present study used wild-type (WT) mice or mutant mice sustaining knockout of either GHR [GHR((-/-)) ] or of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor [GHS-R((-/-)) ] and subjected to FR or not to evaluate the role of GHR and GHS-R in cocaine-stimulated locomotion. WT, GHR((-/-)) , and GHS-R((-/-)) mice were either restricted to 60% of baseline caloric intake or allowed to free-feed (FF). Mice were treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5 and 5.0 mg/kg cocaine on separate test days (in random dose order) and forward locomotion was recorded on each drug day for 45 minutes after drug dosing. Food (and water) was available immediately after (but not during) each activity test. For FF mice, there was no interaction between cocaine and GHR status on locomotion. FR-WT mice treated with saline exhibited significant increases in anticipatory locomotion (relative to FF-WT mice), whereas FR-GHS-R((-/-)) mice did not. Cocaine significantly increased locomotion in FR-GHR((-/-)) and FR-GHS-R((-/-)) mice to the levels noted in FR-WT mice. These results suggest that GHS-R activity, but not GHR activity, is required for FR to augment food-associated anticipatory locomotion, but do not support the contention that GHR pathways are required for the capacity of FR to augment the acute effect of cocaine on locomotion.
© 2010 The Authors, Addiction Biology © 2010 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

References
-
- Abizaid A. Ghrelin and dopamine: new insights on the peripheral regulation of appetite. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009;21:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Abizaid A, Liu ZW, Andrews ZB, Shanabrough M, Borok E, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Sleeman MW, Picciotto MR, Tschop MH, Gao XB, Horvath TL. Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:3229–3239. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsen GC, Berman Y, Carr KD. Curve-shift analysis of self-stimulation in food-restricted rats: relationship between daily meal, plasma corticosterone and reward sensitization. Brain Res. 1995;695:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Tschop M, Robinson SM, Heiman ML. Extent and direction of ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier is determined by its unique primary structure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;302:822–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

