DNA double-strand break signaling and human disorders
- PMID: 21054854
- PMCID: PMC2993650
- DOI: 10.1186/2041-9414-1-15
DNA double-strand break signaling and human disorders
Abstract
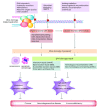
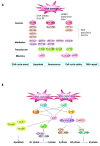
DNA double-strand breaks are among the most serious types of DNA damage and their signaling and repair is critical for all cells and organisms. The repair of both induced and programmed DNA breaks is fundamental as demonstrated by the many human syndromes, neurodegenerative diseases, immunodeficiency and cancer associated with defective repair of these DNA lesions. Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways are the two major DNA repair pathways responsible for mediating the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. The signaling of DNA double-strand breaks is critical for cells to orchestrate the repair pathways and maintain genomic integrity. This signaling network is highly regulated and involves a growing number of proteins and elaborated posttranslational modifications including phosphorylation and ubiquitylation. Here, we highlight the recent progress in the signaling of DNA double-strand breaks, the major proteins and posttranslational modifications involved and the diseases and syndromes associated with impaired signaling of these breaks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extensive ssDNA end formation at DNA double-strand breaks in non-homologous end-joining deficient cells during the S phase.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 26;8:97. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-97. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17963495 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6 is a DNA double-strand break sensor.Elife. 2020 Jan 29;9:e51636. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51636. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31995034 Free PMC article.
-
[Double strand break repair, one mechanism can hide another: alternative non-homologous end joining].Cancer Radiother. 2012 Feb;16(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2011.05.004. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Cancer Radiother. 2012. PMID: 21737335 Review. French.
-
Genomic rearrangements induced by unscheduled DNA double strand breaks in somatic mammalian cells.FEBS J. 2017 Aug;284(15):2324-2344. doi: 10.1111/febs.14053. Epub 2017 Mar 22. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28244221 Review.
-
Kinesin Kif2C in regulation of DNA double strand break dynamics and repair.Elife. 2020 Jan 17;9:e53402. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53402. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31951198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chromosomal Rearrangements and Chromothripsis: The Alternative End Generation Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 2;24(1):794. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010794. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein co-aggregates of dense core amyloid plaques and CSF differ in rapidly progressive Alzheimer's disease and slower sporadic Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 May 27;17(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01767-x. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40420296 Free PMC article.
-
RNF8 induces β-catenin-mediated c-Myc expression and promotes colon cancer proliferation.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 May 1;16(12):2051-2062. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44119. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549753 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Instability Evolutionary Footprints on Human Health: Driving Forces or Side Effects?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11437. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411437. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of Blm and Mus81 in development, fertility, genomic integrity and cancer suppression.Oncogene. 2015 Apr 2;34(14):1780-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.121. Epub 2014 May 26. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24858046
References
-
- Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV Jr, Karakaidos P, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Venere M, Ditullio RA, Kastrinakis NG, Levy B. et al.Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature. 2005;434(7035):907–913. doi: 10.1038/nature03485. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC. et al.Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444(7119):633–637. doi: 10.1038/nature05268. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
