Palmitate and insulin synergistically induce IL-6 expression in human monocytes
- PMID: 21054880
- PMCID: PMC2988002
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-73
Palmitate and insulin synergistically induce IL-6 expression in human monocytes
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance is associated with a proinflammatory state that promotes the development of complications such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and atherosclerosis. The metabolic stimuli that initiate and propagate proinflammatory cytokine production and the cellular origin of proinflammatory cytokines in insulin resistance have not been fully elucidated. Circulating proinflammatory monocytes show signs of enhanced inflammation in obese, insulin resistant subjects and are thus a potential source of proinflammatory cytokine production. The specific, circulating metabolic factors that might stimulate monocyte inflammation in insulin resistant subjects are poorly characterized. We have examined whether saturated nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) and insulin, which increase in concentration with developing insulin resistance, can trigger the production of interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in human monocytes.
Methods: Messenger RNA and protein levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α were measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Luminex bioassays. Student's t-test was used with a significance level of p < 0.05 to determine significance between treatment groups.
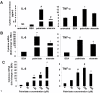
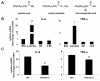
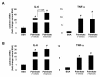
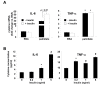
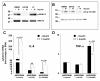
Results: Esterification of palmitate with coenzyme A (CoA) was necessary, while β-oxidation and ceramide biosynthesis were not required, for the induction of IL-6 and TNF-α in THP-1 monocytes. Monocytes incubated with insulin and palmitate together produced more IL-6 mRNA and protein, and more TNF-α protein, compared to monocytes incubated with palmitate alone. Incubation of monocytes with insulin alone did not affect the production of IL-6 or TNF-α. Both PI3K-Akt and MEK/ERK signalling pathways are important for cytokine induction by palmitate. MEK/ERK signalling is necessary for synergistic induction of IL-6 by palmitate and insulin.
Conclusions: High levels of saturated NEFA, such as palmitate, when combined with hyperinsulinemia, may activate human monocytes to produce proinflammatory cytokines and support the development and propagation of the subacute, chronic inflammatory state that is characteristic of insulin resistance. Results with inhibitors of β-oxidation and ceramide biosynthesis pathways suggest that increased fatty acid flux through the glycerolipid biosynthesis pathway may be involved in promoting proinflammatory cytokine production in monocytes.
Figures
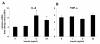
References
-
- Reaven GM. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:473–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

