Expressions and clinical significances of CD133 protein and CD133 mRNA in primary lesion of gastric adenocacinoma
- PMID: 21054902
- PMCID: PMC2987897
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-141
Expressions and clinical significances of CD133 protein and CD133 mRNA in primary lesion of gastric adenocacinoma
Abstract
Background: To study on expressions and clinical significances of CD133 protein and CD133 mRNA in primary lesion of gastric adenocarcinoma (GC).
Methods: Expressions of CD133 protein by immunostaining (99 cases) and CD133 mRNA by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (31 cases) were detected in primary lesion and in noncancerous gastric mucosa tissue (NCGT). Correlations of CD133 protein expression with clinicopathological parameters and post-operative survival were analyzed. Relations of CD133 mRNA level with Ki-67 labeling index (LI), and lymphatic metastasis were assessed too.
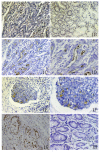
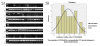
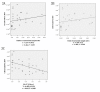
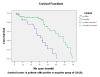
Results: Brown particles indicating CD133 protein positivity occurred in some parts of tumor cells and epithelium. Expressive percentage of CD133 protein positivity was significantly higher in subgroups with >5 cm diameter (P = 0.041), later TNM stage (P = 0.044), severer lymph node metastasis (P = 0.017), occurrences of lymphatic invasion (P = 0.000) and vascular invasion (P = 0.000) respectively. Severer invasion depth (P = 0.011), lymph node metastasis occurrence (P = 0.043) and later TNM stage (P = 0.049) were the independent risk factors for CD133 protein expression. Average brightness scale value (BSV) of CD133 mRNA was significantly higher in subgroups with >5 cm diameter (P = 0.041), lymph node metastasis occurrence (P = 0.004) and in lower Ki-67 LI (P = 0.02). Relative analysis revealed that BSV of CD133 mRNA related positively to metastatic lymphatic nodes ratio (P = 0.008) and metastatic lymph node number (P = 0.009), but negatively to Ki-67 LI (P = 0.009). Survival of positive subgroup of CD 133 protein was significantly poorer (P = 0.047). Lymph node metastasis occurrence (P = 0.042), later TNM stage (P = 0.046) and CD 133 protein positive expression (P = 0.046) were respectively the independent risk factors to survival.
Conclusion: Higher expressive level of CD133 mRNA is associated to lower Ki-67 LI and severer lymphatic metastasis. Therefore, the expressive level of CD133 mRNA can play an appropriate role to reflect the status of lymph node metastasis and proliferation of GC. CD133 protein expression is closely related with larger tumor, later TNM stage, lymphtic metastasis and survival of GC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expressions and clinical significances of c-MET, p-MET and E2f-1 in human gastric carcinoma.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jan 6;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-6. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 24393368 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of CD133 protein correlates with Ki-67 expression and is a prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 20;10:218. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-218. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20487522 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of EphA3 and CD133 expression in colorectal carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2011 Jun;64(6):498-503. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2010.087213. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Clin Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21415057
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of TIMP1 expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024 Nov;24(11):1169-1176. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2024.2408278. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 39305243
-
Clinicopathological features of hepatoid adenocarcinoma and non-hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2024 Aug;13(16):e70130. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70130. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39186327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and CD133 predicts pathological complete response and survival for locally advanced rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Jan 25;46(1):36-43. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2017.02.06. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 28436629 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD133 in patients with gastric cancer: A comprehensive meta-analysis with 4729 patients involved.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(42):e5163. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005163. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27759647 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter hypermethylation of CD133/PROM1 is an independent poor prognosis factor for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e19491. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019491. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176088 Free PMC article.
-
CD133 Expression as a Helicobacter pylori-independent Biomarker of Gastric Cancer Progression.Anticancer Res. 2018 Aug;38(8):4443-4448. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12746. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30061208 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CD133 as a cancer stem cell marker in invasive gastric carcinoma.Pathologica. 2019 Mar;111(1):18-23. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-51-18. Pathologica. 2019. PMID: 31217618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fidler IJ. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6130–6138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

