A dominant mutation in the gene encoding the erythroid transcription factor KLF1 causes a congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
- PMID: 21055716
- PMCID: PMC2978953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.10.010
A dominant mutation in the gene encoding the erythroid transcription factor KLF1 causes a congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
Abstract
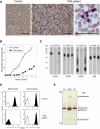
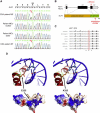
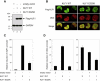
The congenital dyserythropoietic anemias (CDAs) are inherited red blood cell disorders whose hallmarks are ineffective erythropoiesis, hemolysis, and morphological abnormalities of erythroblasts in bone marrow. We have identified a missense mutation in KLF1 of patients with a hitherto unclassified CDA. KLF1 is an erythroid transcription factor, and extensive studies in mouse models have shown that it plays a critical role in the expression of globin genes, but also in the expression of a wide spectrum of genes potentially essential for erythropoiesis. The unique features of this CDA confirm the key role of KLF1 during human erythroid differentiation. Furthermore, we show that the mutation has a dominant-negative effect on KLF1 transcriptional activity and unexpectedly abolishes the expression of the water channel AQP1 and the adhesion molecule CD44. Thus, the study of this disease-causing mutation in KLF1 provides further insights into the roles of this transcription factor during erythropoiesis in humans.
Copyright © 2010 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Renella R., Wood W.G. The congenital dyserythropoietic anemias. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2009;23:283–306. - PubMed
-
- Heimpel H., Wendt F., Klemm D., Schubothe H., Heilmeyer L. Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia. Arch. Klin. Med. 1968;215:174–194. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz K., Iolascon A., Verissimo F., Trede N.S., Horsley W., Chen W., Paw B.H., Hopfner K.P., Holzmann K., Russo R. Mutations affecting the secretory COPII coat component SEC23B cause congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type II. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:936–940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

