Mutations in myosin light chain kinase cause familial aortic dissections
- PMID: 21055718
- PMCID: PMC2978973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.10.006
Mutations in myosin light chain kinase cause familial aortic dissections
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Apr 8;88(4):516
Abstract
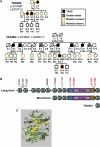
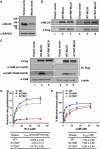
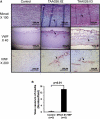
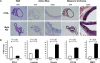
Mutations in smooth muscle cell (SMC)-specific isoforms of α-actin and β-myosin heavy chain, two major components of the SMC contractile unit, cause familial thoracic aortic aneurysms leading to acute aortic dissections (FTAAD). To investigate whether mutations in the kinase that controls SMC contractile function (myosin light chain kinase [MYLK]) cause FTAAD, we sequenced MYLK by using DNA from 193 affected probands from unrelated FTAAD families. One nonsense and four missense variants were identified in MYLK and were not present in matched controls. Two variants, p.R1480X (c.4438C>T) and p.S1759P (c.5275T>C), segregated with aortic dissections in two families with a maximum LOD score of 2.1, providing evidence of linkage of these rare variants to the disease (p = 0.0009). Both families demonstrated a similar phenotype characterized by presentation with an acute aortic dissection with little to no enlargement of the aorta. The p.R1480X mutation leads to a truncated protein lacking the kinase and calmodulin binding domains, and p.S1759P alters amino acids in the α-helix of the calmodulin binding sequence, which disrupts kinase binding to calmodulin and reduces kinase activity in vitro. Furthermore, mice with SMC-specific knockdown of Mylk demonstrate altered gene expression and pathology consistent with medial degeneration of the aorta. Thus, genetic and functional studies support the conclusion that heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in MYLK are associated with aortic dissections.
Copyright © 2010 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dissecting the genes of familial aortic dissections.Clin Genet. 2011 May;79(5):425-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01629.x. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Clin Genet. 2011. PMID: 21231930 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kamm K.E., Stull J.T. Dedicated myosin light chain kinases with diverse cellular functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:4527–4530. - PubMed
-
- Schubert R., Lidington D., Bolz S.S. The emerging role of Ca2+ sensitivity regulation in promoting myogenic vasoconstriction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008;77:8–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

