Delay of migrating leukocytes by the basement membrane deposited by endothelial cells in long-term culture
- PMID: 21056557
- PMCID: PMC3025349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.10.022
Delay of migrating leukocytes by the basement membrane deposited by endothelial cells in long-term culture
Abstract
We investigated the migration of human leukocytes through endothelial cells (EC), and particularly their underlying basement membrane (BM). EC were cultured for 20days on 3μm-pore filters or collagen gels to form a distinct BM, and then treated with tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β or interferon-γ. Neutrophil migration through the cytokine-treated EC and BM was delayed for 20-day compared to 4-day cultures. The BM alone obstructed chemotaxis of neutrophils, and if fresh EC were briefly cultured on stripped BM, there was again a hold-up in migration. In studies with lymphocytes and monocytes, we could detect little hold-up of migration for 20-day versus 4-day cultures, in either the filter- or gel-based models. Direct microscopic observations showed that BM also held-up neutrophil migration under conditions of flow. Treatment of upper and/or lower compartments of filters with antibodies against integrins, showed that neutrophil migration through the endothelial monolayer was dependent on β(2)-integrins, but not β1- or β(3)-integrins. Migration from the subendothelial compartment was supported by β1- and β(2)-integrins for all cultures, but blockade of β(3)-integrin only inhibited migration effectively for 20-day cultures. Flow cytometry indicated that there was no net increase in expression of β1- or β3-integrins during neutrophil migration, and that their specific subendothelial function was likely dependent on turnover of integrins during migration. These studies show that BM is a distinct barrier to migration of human neutrophils, and that β(3)-integrins are particularly important in crossing this barrier. The lesser effect of BM on lymphocytes and monocytes supports the concept that crossing the BM is a separate, leukocyte-specific, regulated step in migration.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
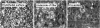
 ) or 20 (
) or 20 ( ) days and then treated with TNF or IL-1. A,B. Scanning electron micrographs of matrix deposited by EC on filters after culture for 4 days or 20 days. C. Transmigration after 2 h through HUVEC treated with different doses of TNF. D. Time course of transmigration through HUVEC treated with 100 U/ml TNF. E. Comparison of transmigration through HUVEC treated with TNF (100 U/ml) or IL-1 (50 pg/ml). F. Effect of adding IL-8 to the bottom well on transmigration through HUVEC treated with TNF (100 U/ml). Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 to 7 independent experiments. In C, ANOVA showed a significant effect of TNF dose (p < 0.01) and culture duration (p < 0.01). In D, ANOVA showed a significant effect of culture duration (p < 0.05) and assay time (p < 0.01). In E and F, ANOVA showed significant effects of culture duration (p < 0.01). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to 4-day by paired t-test.
) days and then treated with TNF or IL-1. A,B. Scanning electron micrographs of matrix deposited by EC on filters after culture for 4 days or 20 days. C. Transmigration after 2 h through HUVEC treated with different doses of TNF. D. Time course of transmigration through HUVEC treated with 100 U/ml TNF. E. Comparison of transmigration through HUVEC treated with TNF (100 U/ml) or IL-1 (50 pg/ml). F. Effect of adding IL-8 to the bottom well on transmigration through HUVEC treated with TNF (100 U/ml). Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 to 7 independent experiments. In C, ANOVA showed a significant effect of TNF dose (p < 0.01) and culture duration (p < 0.01). In D, ANOVA showed a significant effect of culture duration (p < 0.05) and assay time (p < 0.01). In E and F, ANOVA showed significant effects of culture duration (p < 0.01). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to 4-day by paired t-test.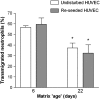
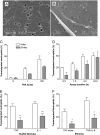
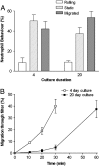
 ) or 20 days (
) or 20 days ( ) and then treated with TNF + IFNγ. Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments in which migration was analysed after 2, 4 and 24 h.
) and then treated with TNF + IFNγ. Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments in which migration was analysed after 2, 4 and 24 h.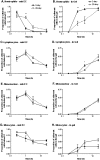
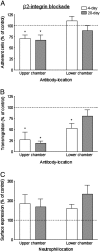
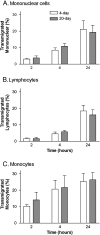
 ) and 20-day (
) and 20-day ( ) cultures are shown, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of the upper chamber; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of either type; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 3 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of either type, but there was no significant effect of treatment for the individual days.
) cultures are shown, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of the upper chamber; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of either type; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 3 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of either type, but there was no significant effect of treatment for the individual days.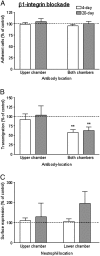
 ) and 20-day (
) and 20-day ( ) cultures are shown, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of both chambers; **p < 0.01 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 3 experiments.
) cultures are shown, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 5 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of both chambers; **p < 0.01 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 3 experiments.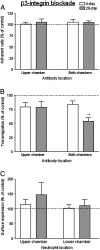
 ) and 20-day (
) and 20-day ( ) cultures, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 6 experiments. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 6 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of the both chambers; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 4 experiments.
) cultures, expressed relative to untreated control. In A, data are the mean ± SEM from 6 experiments. In B, data are the mean ± SEM from 6 experiments. ANOVA showed a significant effect of treatment of the both chambers; *p < 0.05 compared to control by paired t-test. In C, data are the mean ± SEM from 4 experiments.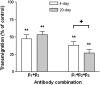
 ) and 20-day (
) and 20-day ( ) cultures, expressed relative to untreated control. Data are the mean ± SEM from 4 experiments. **p < 0.01 compared to control by paired t-test. +p < 0.05 for comparison between 4-day and 20-day cultures by paired t-test.
) cultures, expressed relative to untreated control. Data are the mean ± SEM from 4 experiments. **p < 0.01 compared to control by paired t-test. +p < 0.05 for comparison between 4-day and 20-day cultures by paired t-test.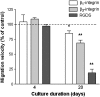
 ) or β3-integrin (
) or β3-integrin ( ) was added to neutrophils before perfusion, but was absent from washout medium. RGDS peptide (
) was added to neutrophils before perfusion, but was absent from washout medium. RGDS peptide ( ) was added to neutrophils before perfusion and was also present in washout medium. Data are the mean ± SEM of the mean velocities relative to untreated controls from 3 experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to untreated cells by paired t-test.
) was added to neutrophils before perfusion and was also present in washout medium. Data are the mean ± SEM of the mean velocities relative to untreated controls from 3 experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to untreated cells by paired t-test.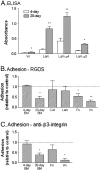
 ) or 20 days (
) or 20 days ( ). B. shows effect of RGDS peptide on adhesion of neutrophils to 4-day or 20-day BM, collagen type IV (Coll), laminin (Lam), fibronectin (Fn) or vitronectin (Vn). C. shows effect of antibody against β3-integrin on adhesion to 4-day or 20-day BM, fibronectin (Fn) or vitronectin (Vn). In B and C, adhesion is expressed relative to untreated control. Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 or more experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to 4-day in A, or untreated control in B and C, by paired t-test.
). B. shows effect of RGDS peptide on adhesion of neutrophils to 4-day or 20-day BM, collagen type IV (Coll), laminin (Lam), fibronectin (Fn) or vitronectin (Vn). C. shows effect of antibody against β3-integrin on adhesion to 4-day or 20-day BM, fibronectin (Fn) or vitronectin (Vn). In B and C, adhesion is expressed relative to untreated control. Data are the mean ± SEM from 3 or more experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to 4-day in A, or untreated control in B and C, by paired t-test.Similar articles
-
Effects of endothelial basement membrane on neutrophil adhesion and migration.Cell Immunol. 2008 Jan;251(1):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 May 13. Cell Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18479679
-
Prolonged culture of endothelial cells and deposition of basement membrane modify the recruitment of neutrophils.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Oct 15;310(1):22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.07.001. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 16109405
-
Blockade of alpha 5 beta 1 integrins reverses the inhibitory effect of tenascin on chemotaxis of human monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes through three-dimensional gels of extracellular matrix proteins.J Immunol. 2001 Jun 15;166(12):7534-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7534. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11390508
-
Integrin-dependent neutrophil migration in the injured mouse cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2014 Mar;120:61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Exp Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24462632 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic regulation of leukocyte motility and migration.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Aug;104(2):285-293. doi: 10.1002/JLB.1MR1117-472R. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29451682 Review.
Cited by
-
Microvascular Mimetics for the Study of Leukocyte-Endothelial Interactions.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020 Jan 31;13(2):125-139. doi: 10.1007/s12195-020-00611-6. eCollection 2020 Apr. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 32175026 Free PMC article.
-
Crosslinking of membrane CD13 in human neutrophils mediates phagocytosis and production of reactive oxygen species, neutrophil extracellular traps and proinflammatory cytokines.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:994496. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.994496. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439182 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of integrins in function of human neutrophils after their migration through endothelium into interstitial matrix.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 23;10(2):e0118593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118593. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25706870 Free PMC article.
-
Human Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Neuroregeneration in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8583. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158583. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955732 Free PMC article.
-
On, around, and through: neutrophil-endothelial interactions in innate immunity.Physiology (Bethesda). 2011 Oct;26(5):334-47. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00011.2011. Physiology (Bethesda). 2011. PMID: 22013192 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith C.W., Kishimoto T.K., Abbassi O., Hughes B., Rothlein R., McIntire L.V., Butcher E., Anderson D.C., Abbass O. Chemotactic factors regulate lectin adhesion molecule 1 (LECAM-1)-dependent neutrophil adhesion to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 1991;87:609–618. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luscinskas F.W., Ding H., Tan P., Cumming D., Tedder T.F., Gerritsen M.E. L- and P-selectins, but not CD49d (VLA-4) integrins, mediate monocyte initial attachment to TNF-alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow in vitro. J. Immunol. 1996;157:326–335. - PubMed
-
- Springer T.A. Traffic signals on endothelium for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1995;57:827–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

