Computational analysis and identification of an emergent human adenovirus pathogen implicated in a respiratory fatality
- PMID: 21056888
- PMCID: PMC3006489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.10.020
Computational analysis and identification of an emergent human adenovirus pathogen implicated in a respiratory fatality
Abstract
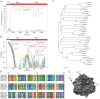
Adenoviral infections are typically acute, self-limiting, and not associated with death. However, we present the genomic and bioinformatics analysis of a novel recombinant human adenovirus (HAdV-D56) isolated in France that caused a rare neonatal fatality, and keratoconjunctivitis in three health care workers who cared for the neonate. Whole genome alignments revealed the expected diversity in the penton base, hexon, E3, and fiber coding regions, and provided evidence for extensive recombination. Bootscan analysis confirmed recombination between HAdV-D9, HAdV-D26, HAdV-D15, and HAdV-D29 in the penton base and hexon proteins, centered around hypervariable loops within the putative proteins. Protein structure analysis of the fiber coding region revealed similarity with HAdV-D8, HAdV-D9, and HAdV-D53, possibly accounting for the ocular tropism of the virus. Based on these data, this virus appears to be a new HAdV-D type (HAdV-D56), underscoring the importance of recombination events in human adenovirus evolution and the emergence of new adenovirus pathogens.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Abbondanzo SL, English CK, Kagan E, McPherson RA. Fatal adenovirus pneumonia in a newborn identified by electron microscopy and in situ hybridization. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989;113(12):1349–53. - PubMed
-
- Abzug MJ, Levin MJ. Neonatal adenovirus infection: four patients and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 1991;87(6):890–6. - PubMed
-
- Adrian T, Bastian B, Benoist W, Hierholzer JC, Wigand R. Characterization of adenovirus 15/H9 intermediate strains. Intervirology. 1985;23(1):15–22. - PubMed
-
- Arnberg N, Kidd AH, Edlund K, Nilsson J, Pring-Akerblom P, Wadell G. Adenovirus type 37 binds to cell surface sialic acid through a charge-dependent interaction. Virology. 2002;302(1):33–43. - PubMed
-
- Arnberg N, Mei Y, Wadell G. Fiber genes of adenoviruses with tropism for the eye and the genital tract. Virology. 1997;227(1):239–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

