Xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase-mediated xyloglucan rearrangements in developing wood of hybrid aspen
- PMID: 21057113
- PMCID: PMC3075792
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.166934
Xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase-mediated xyloglucan rearrangements in developing wood of hybrid aspen
Abstract
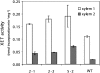
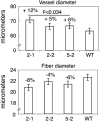
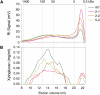
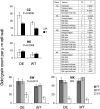
Xyloglucan endo-transglycosylases (XETs) encoded by xyloglucan endo-transglycosylases/hydrolase (XTH) genes modify the xyloglucan-cellulose framework of plant cell walls, thereby regulating their expansion and strength. To evaluate the importance of XET in wood development, we studied xyloglucan dynamics and XTH gene expression in developing wood and modified XET activity in hybrid aspen (Populus tremula × tremuloides) by overexpressing PtxtXET16-34. We show that developmental modifications during xylem differentiation include changes from loosely to tightly bound forms of xyloglucan and increases in the abundance of fucosylated xyloglucan epitope recognized by the CCRC-M1 antibody. We found that at least 16 Populus XTH genes, all likely encoding XETs, are expressed in developing wood. Five genes were highly and ubiquitously expressed, whereas PtxtXET16-34 was expressed more weakly but specifically in developing wood. Transgenic up-regulation of XET activity induced changes in cell wall xyloglucan, but its effects were dependent on developmental stage. For instance, XET overexpression increased abundance of the CCRC-M1 epitope in cambial cells and xylem cells in early stages of differentiation but not in mature xylem. Correspondingly, an increase in tightly bound xyloglucan content was observed in primary-walled xylem but a decrease was seen in secondary-walled xylem. Thus, in young xylem cells, XET activity limits xyloglucan incorporation into the tightly bound wall network but removes it from cell walls in older cells. XET overexpression promoted vessel element growth but not fiber expansion. We suggest that the amount of nascent xyloglucan relative to XET is an important determinant of whether XET strengthens or loosens the cell wall.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase (XET) functions in gelatinous layers of tension wood fibers in poplar--a glimpse into the mechanism of the balancing act of trees.Plant Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;48(6):843-55. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcm055. Epub 2007 May 15. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17504814
-
XTH31, encoding an in vitro XEH/XET-active enzyme, regulates aluminum sensitivity by modulating in vivo XET action, cell wall xyloglucan content, and aluminum binding capacity in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Nov;24(11):4731-47. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.106039. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 23204407 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of xylan endotransglycosylase PtxtXyn10A affects cellulose microfibril angle in secondary wall in aspen wood.New Phytol. 2015 Jan;205(2):666-81. doi: 10.1111/nph.13099. Epub 2014 Oct 13. New Phytol. 2015. PMID: 25307149
-
Broad Specific Xyloglucan:Xyloglucosyl Transferases Are Formidable Players in the Re-Modelling of Plant Cell Wall Structures.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 31;23(3):1656. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031656. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The XTH family of enzymes involved in xyloglucan endotransglucosylation and endohydrolysis: current perspectives and a new unifying nomenclature.Plant Cell Physiol. 2002 Dec;43(12):1421-35. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcf171. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12514239 Review.
Cited by
-
WRKY1 acts as a key component improving resistance against Alternaria solani in wild tomato, Solanum arcanum Peralta.Plant Biotechnol J. 2018 Aug;16(8):1502-1513. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12892. Epub 2018 May 24. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29377467 Free PMC article.
-
Peach Fruit Development: A Comparative Proteomic Study Between Endocarp and Mesocarp at Very Early Stages Underpins the Main Differential Biochemical Processes Between These Tissues.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jun 4;10:715. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00715. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31214229 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of transcriptome dynamics during watermelon fruit development: sequencing, assembly, annotation and gene expression profiles.BMC Genomics. 2011 Sep 21;12:454. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-454. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21936920 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor PagMYB31 positively regulates cambium activity and negatively regulates xylem development in poplar.Plant Cell. 2024 May 1;36(5):1806-1828. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae040. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38339982 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Analysis of the Xyloglucan Endotransglucosylase/Hydrolase Gene Family in Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.).Genes (Basel). 2018 May 24;9(6):273. doi: 10.3390/genes9060273. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29795009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba K, Park YW, Kaku T, Kaida R, Takeuchi M, Yoshida M, Hosoo Y, Ojio Y, Okuyama T, Taniguchi T, et al. (2009) Xyloglucan for generating tensile stress to bend tree stem. Mol Plant 2: 893–903 - PubMed
-
- Baluška F, Liners F, Hlavacka A, Schlicht M, Van Cutsem P, McCurdy DW, Menzel D. (2005) Cell wall pectins and xyloglucans are internalized into dividing root cells and accumulate within cell plates during cytokinesis. Protoplasma 225: 141–155 - PubMed
-
- Becnel J, Natarajan M, Kipp A, Braam J. (2006) Developmental expression patterns of Arabidopsis XTH genes reported by transgenes and Genevestigator. Plant Mol Biol 61: 451–467 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

