Regulation of MAPK signaling and cell death by MAPK phosphatase MKP2
- PMID: 21057191
- PMCID: PMC3115266
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.5.11.13645
Regulation of MAPK signaling and cell death by MAPK phosphatase MKP2
Abstract
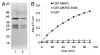
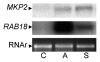
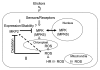
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways play crucial roles in developmental and adaptive responses. Depending on the stimulus, MAPK activation regulates a wide variety of plant cell responses, such as proliferation, differentiation and cell death, which normally require precise spatial and temporal control. In this context, protein phosphatases play important roles by regulating the duration and magnitude of MAPK activities. During infection by non-host and incompatible host microorganisms, MAPK activity can promote a local cell death mechanism called hypersensitivity response (HR), which is part of the plant defence response. HR-like responses require sustained MAPK activity and correlate with oxidative burst. We recently showed that MAPK phosphatase MKP2 positively controls biotic and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. MKP2 interacts with MPK6 in HR-like responses triggered by fungal elicitors, suggesting that MKP2 protein is part of the mechanism involved in MAPK regulation during HR. Here we discuss the interplay of MAPK and MKP2 phosphatase signaling during cell death responses elicited by host-pathogen interactions.
Figures
Comment on
-
MAPK phosphatase MKP2 mediates disease responses in Arabidopsis and functionally interacts with MPK3 and MPK6.Plant J. 2010 Sep;63(6):1017-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04297.x. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20626661
References
-
- Rodriguez MC, Petersen M, Mundy J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:621–649. - PubMed
-
- Gudesblat GE, Iusem ND, Morris PC. Guard cell-specific inhibition of Arabidopsis MPK3 expression causes abnormal stomatal responses to abscisic acid and hydrogen peroxide. New Phytol. 2007;173:713–721. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Wang S, Sritubtim S, Chen JG, Ellis BE. Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK12 interacts with the MAPK phosphatase IBR5 and regulates auxin signaling. Plant J. 2009;57:975–985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
